Creates a lighting specification object for use with 3D polygon layers.
Lighting modifies the brightness of fill and/or base color aesthetics based on surface
orientation (i.e., it implements form shadows but not cast shadows).
Various options are available to control light qualities and light source location.
The result can be passed coord_3d() to for application to the whole plot, or to individual
geom_*_3d() layer functions (which take precedence over plot-level lighting).
Usage
light(
method = "diffuse",
direction = c(-0.5, 0, 1),
position = NULL,
distance_falloff = FALSE,
fill = TRUE,
color = TRUE,
mode = "hsv",
contrast = 1,
backface_scale = -1,
backface_offset = 0
)Arguments
- method
Character string specifying lighting model:
"diffuse": The default. Atmospheric lighting with soft shadows (only surfaces pointing directly away from light source are fully dark; base color occurs on surfaces perpendicular to light)"direct": Direct lighting with hard shadows (all surfaces angled beyond 90 degrees from light source are fully dark; base color occurs on surfaces angled 45 degrees toward light)"rgb": Map surface orientation to three dimensional color space. Rather than the light model darkening or brightening base colors as in the other models, this model generates a wholly new set of colors. If this option is selected, parameters likemodeandcontrastare ignored, butfill,color, anddirectionstill apply.
- direction
Numeric vector of length 3 specifying direction in 3D space that light comes from for directional lighting. The default is
c(1, 0, 1), giving diagonal lighting from the upper right edge with default rotation. Common examples:c(0, 0, 1)gives overhead lighting,c(1, 0, 0)lights surfaces facing the positive x direction, andc(-1, -1, 0)lights surfaces facing negative x-y edge. At least one value must be non-zero. Values are automatically normalized, so magnitude doesn't matter, only sign and relative magnitude. Direction is relative to the data axes, not the rotated figure. This argument is ignored ifpositionis provided.- position
Numeric vector of length 3 specifying light source position in data coordinate space for positional lighting. When specified, each face gets its own light direction calculated from the light position to the face center. Mutually exclusive with
direction. Default is NULL (use directional lighting).- distance_falloff
Logical indicating whether to apply distance-based intensity falloff for positional lighting using inverse square law (intensity ∝ 1/distance²). Only used when
positionis specified. Default is FALSE.- fill
Logical indicating whether to apply lighting to fill colors. Default is TRUE.
- color
Logical indicating whether to apply lighting to border/line colors. Default is TRUE.
- mode
Character string specifying color lighting mode:
"hsv": The default. Modifies value component of HSV color (fades to bright colors at high end, black at low end)."hsl": Modifies lightness component of HSL color (fades to white at high end, black at low end).
These two options give identical results for grayscale colors.
- contrast
Numeric value greater than zero controlling the intensity of lighting effects. 1.0 (the default) gives full black-to-white range. Values less than 1 give subtler effects, while values greater than 1 give more dramatic effects.
- backface_scale, backface_offset
Numeric values that determine how "frontface" light values get modified (scaled and then offset) to derive "backface" light values. A backface is the side of a polygon that faces the underside of a surface or the inside of a volume. Frontface light values are typically in the range
[-1, 1](unlesscontrastis boosted). The default scale of -1 gives backfaces highly contrasting lighting to frontfaces. To light backfaces the same as frontfaces, set scale to 1. To uniformly darken (brighten) all backfaces, use a negative (positive) offset.
Value
A lighting object that can be passed to polygon-based 3D layers or to coord_3d().
Details
Note that light-like effects can also be achieved in some stats by mapping color
aesthestics to computed variables such as after_stat(dzdx); see geom_surface_3d()
for examples.
Examples
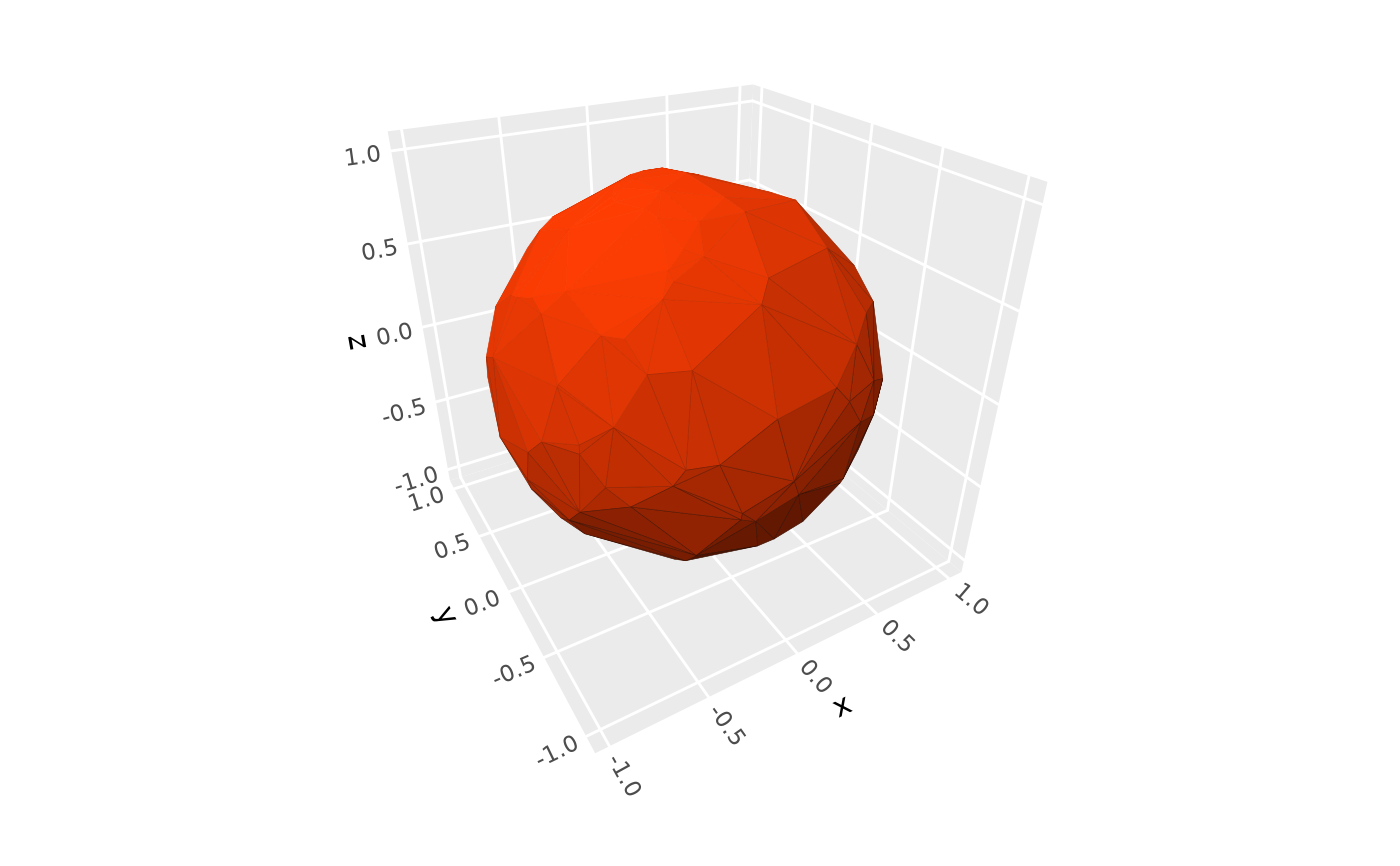
# base plot used in examples
p <- ggplot(sphere_points, aes(x, y, z)) +
geom_hull_3d(fill = "#9e2602", color = "#5e1600")
# Light qualities ----------------------------------------------------------
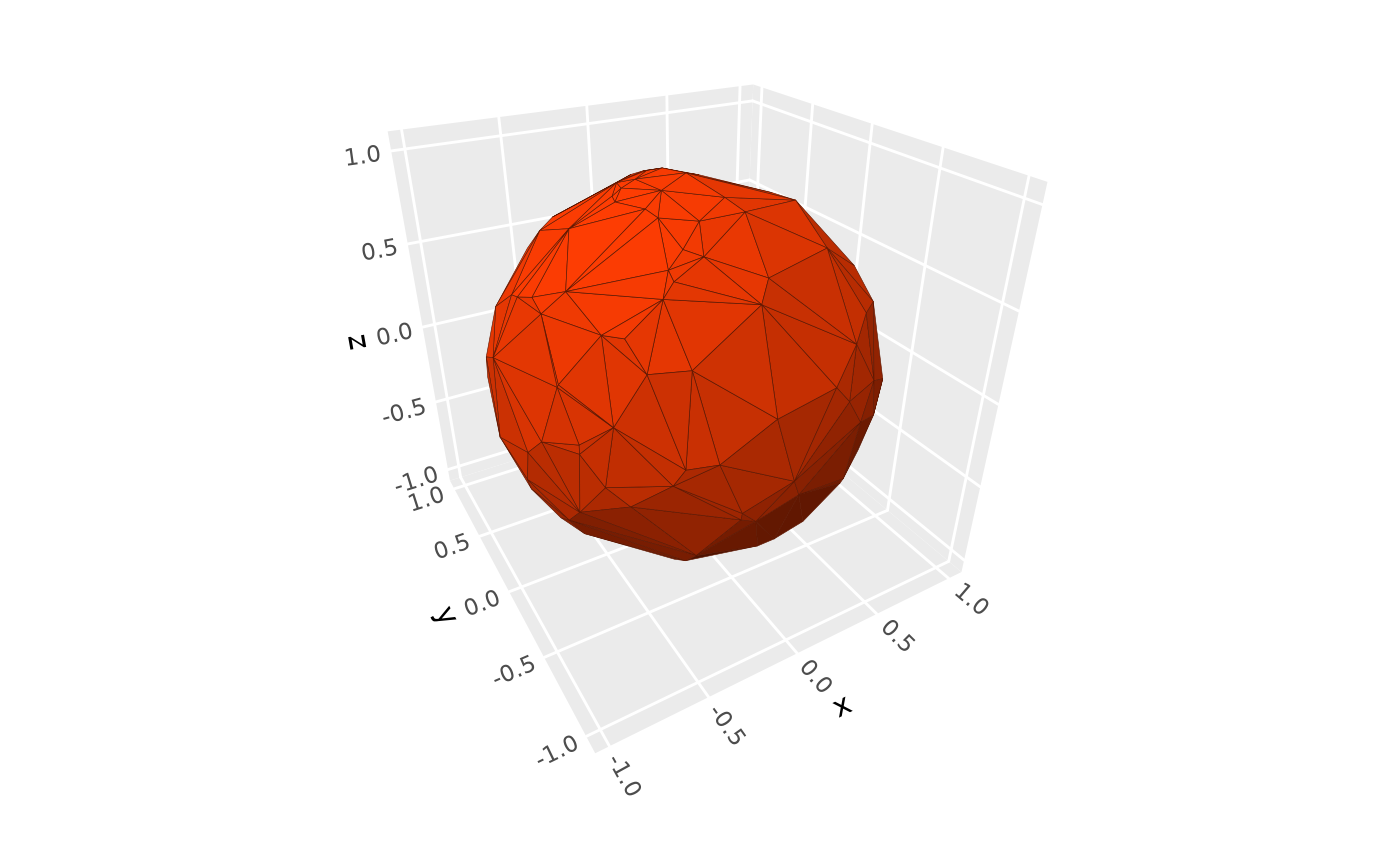
# default `"diffuse"` lighting
p + coord_3d()
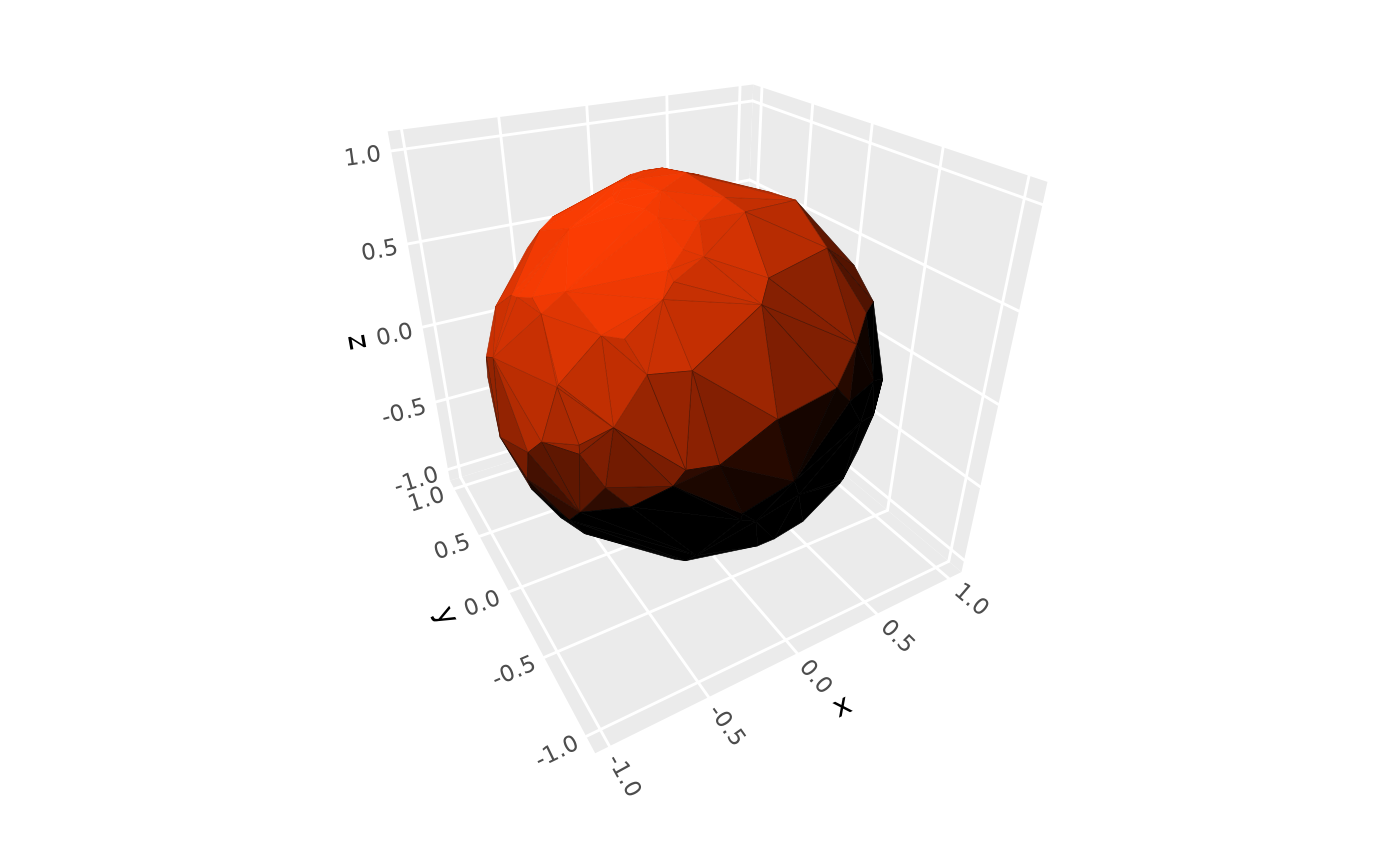
 # use `"direct"` lighting to apply full shade to unlit surfaces
p + coord_3d(light = light(method = "direct"))
# use `"direct"` lighting to apply full shade to unlit surfaces
p + coord_3d(light = light(method = "direct"))
 # use `"hsl"` mode to fade highlights to white
p + coord_3d(light = light(mode = "hsl"))
# use `"hsl"` mode to fade highlights to white
p + coord_3d(light = light(mode = "hsl"))
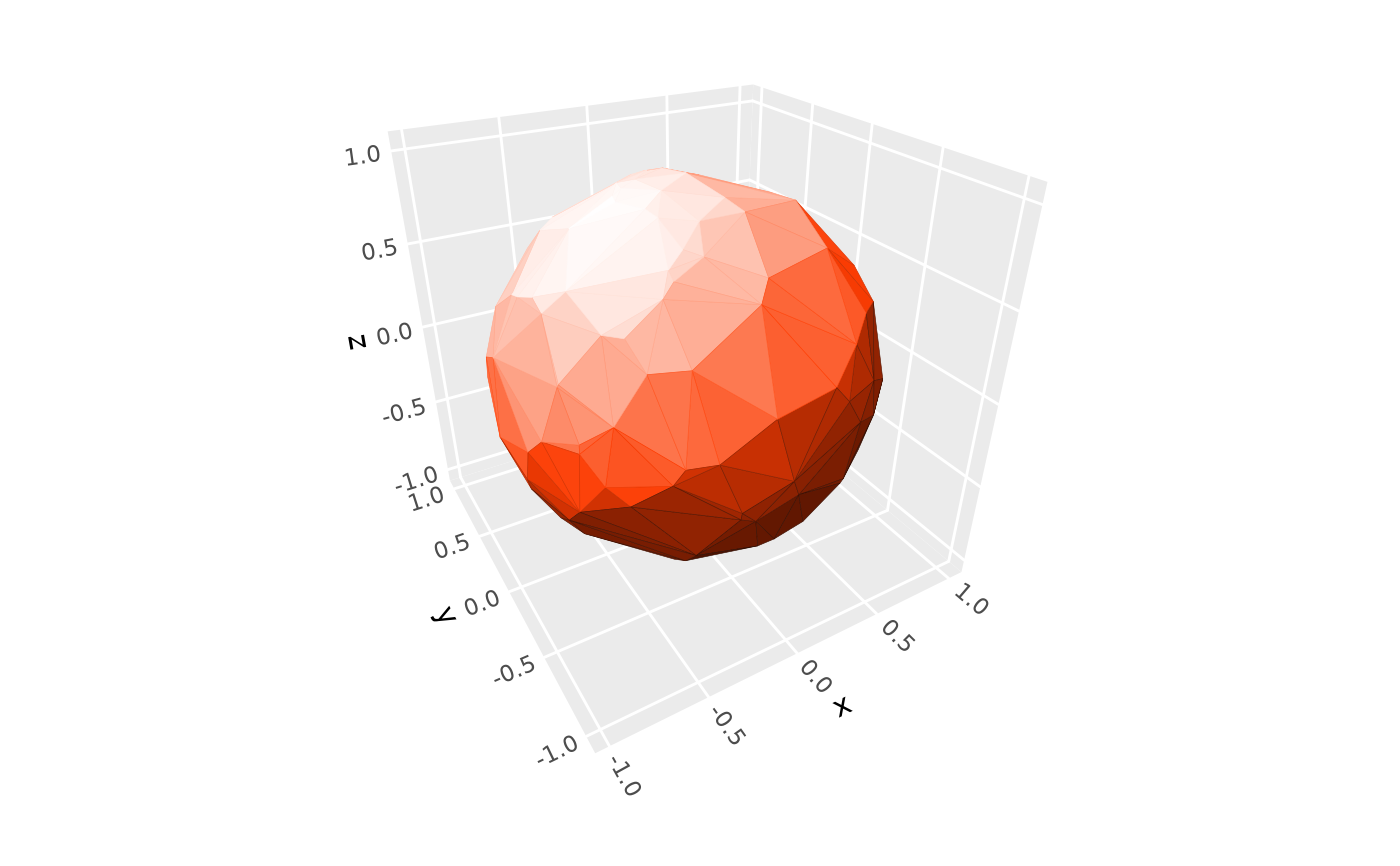 # adjust lighting intensity with `contrast`
p + coord_3d(light = light(mode = "hsl", contrast = 1.5))
# adjust lighting intensity with `contrast`
p + coord_3d(light = light(mode = "hsl", contrast = 1.5))
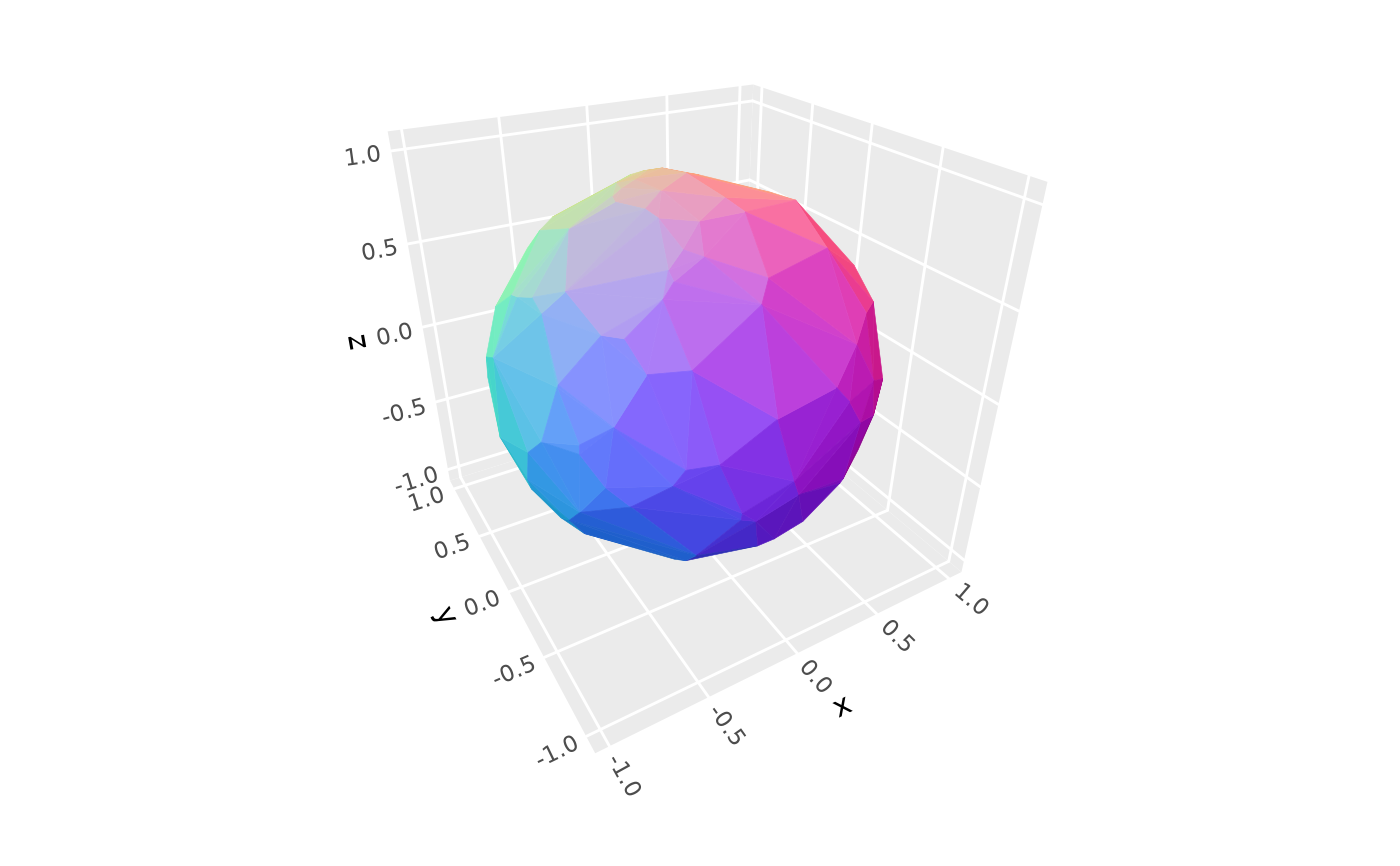
 # use `"rgb"` lighting to map face orientation to 3D color space
p + coord_3d(light = light(method = "rgb"))
# use `"rgb"` lighting to map face orientation to 3D color space
p + coord_3d(light = light(method = "rgb"))
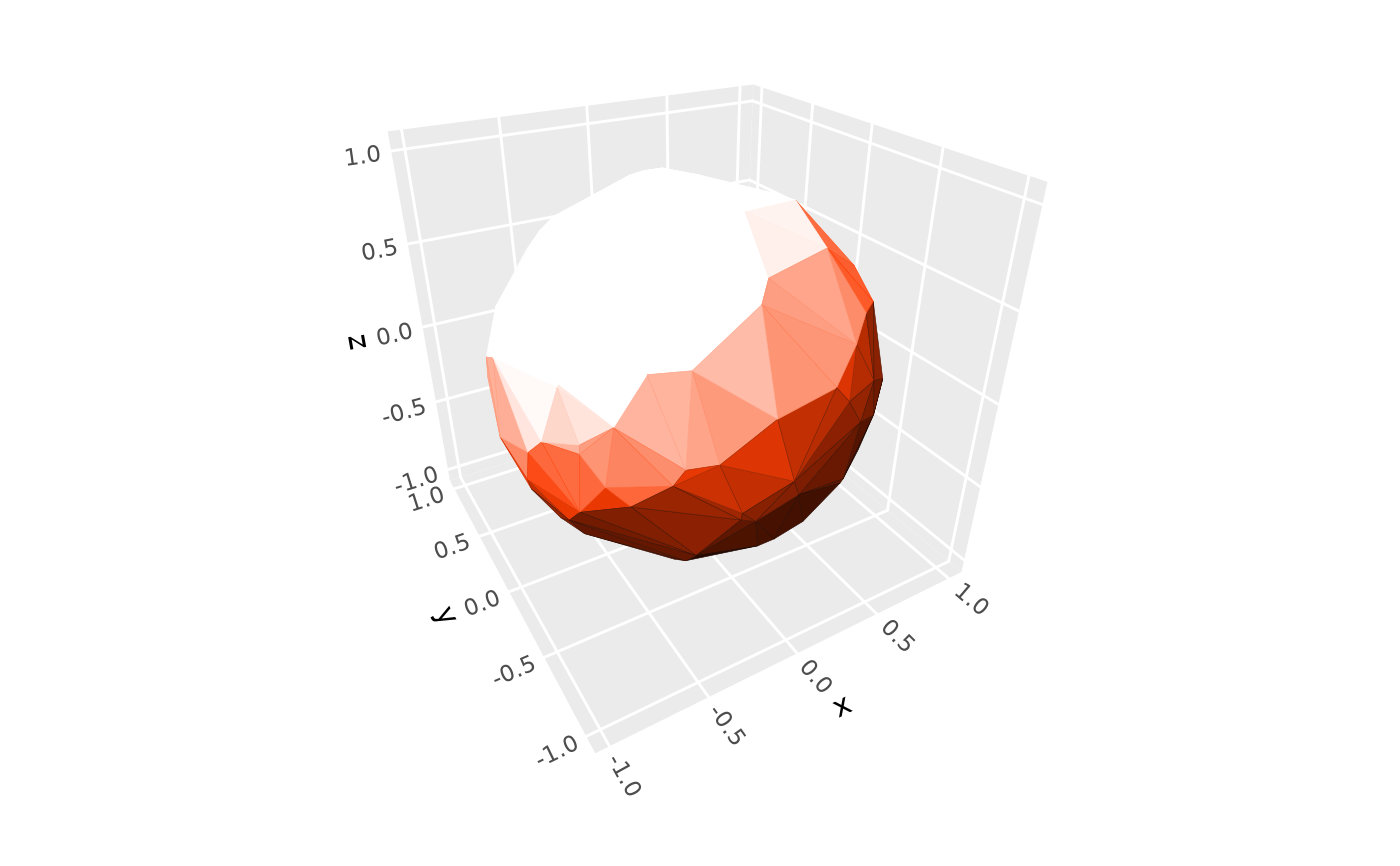
 # Lighting targets ---------------------------------------------------------
# use `fill` and `color` to select which aesthetics get modified by light
p + coord_3d(light = light(fill = TRUE, color = FALSE))
# Lighting targets ---------------------------------------------------------
# use `fill` and `color` to select which aesthetics get modified by light
p + coord_3d(light = light(fill = TRUE, color = FALSE))
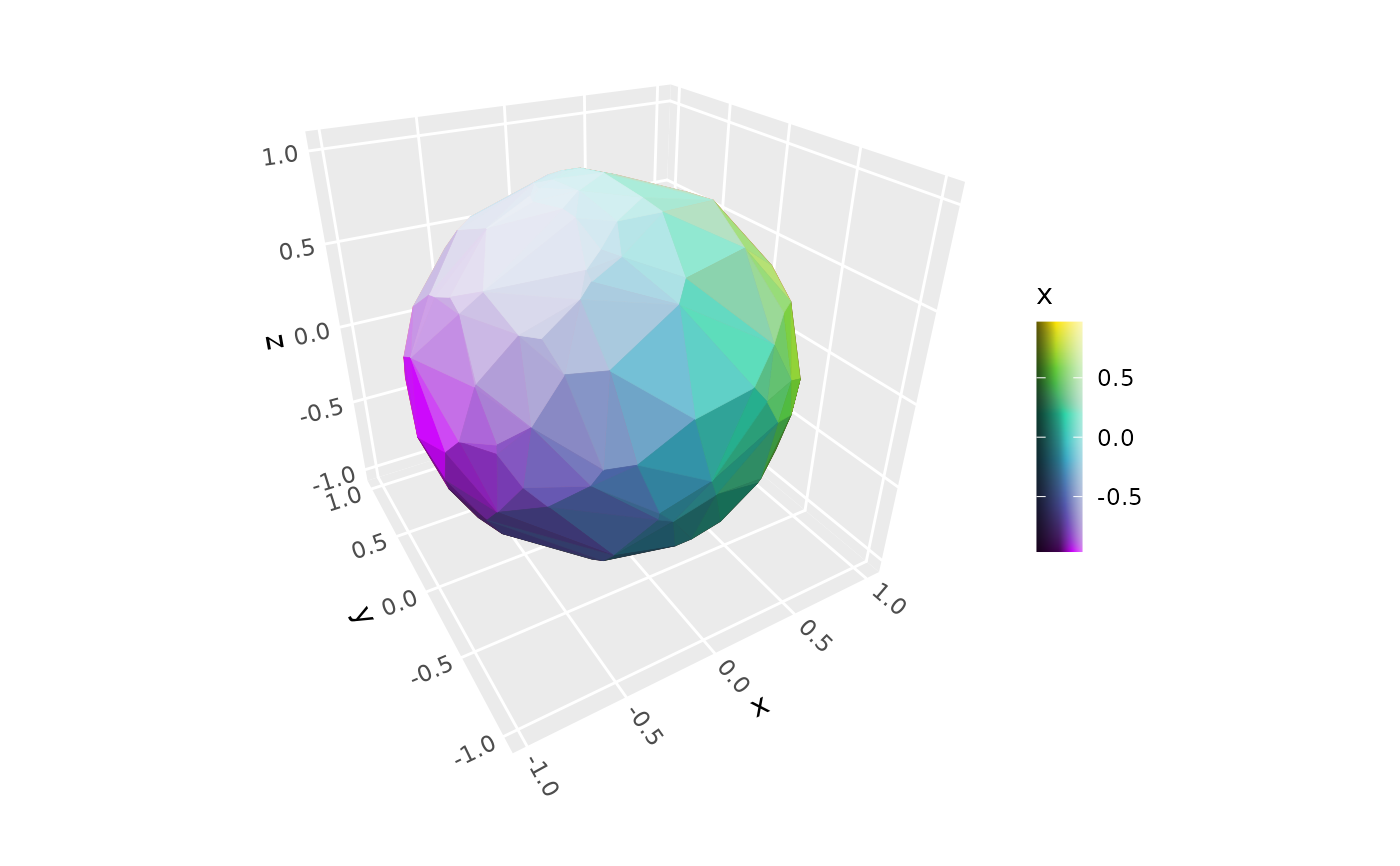
 # apply lighting to aesthetically mapped colors, with shaded guide to match
p + geom_hull_3d(aes(fill = x, color = x)) +
scale_fill_viridis_c() +
scale_color_viridis_c() +
guides(fill = guide_colorbar_3d()) +
coord_3d(light = light(mode = "hsl", contrast = .9))
# apply lighting to aesthetically mapped colors, with shaded guide to match
p + geom_hull_3d(aes(fill = x, color = x)) +
scale_fill_viridis_c() +
scale_color_viridis_c() +
guides(fill = guide_colorbar_3d()) +
coord_3d(light = light(mode = "hsl", contrast = .9))
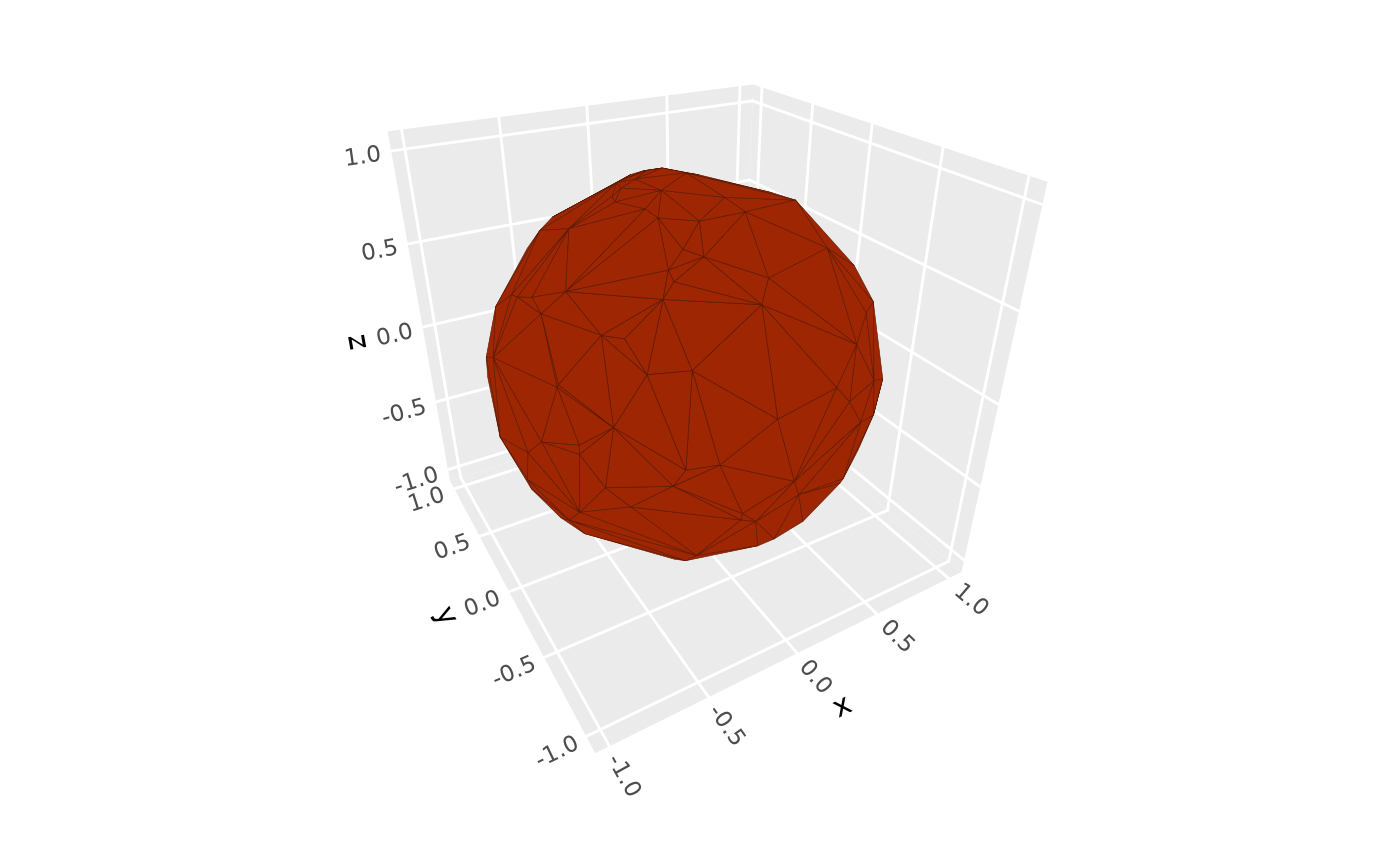
 # disable lighting entirely
# (equivalent to specifying `light(fill = FALSE, color = FALSE`))
p + coord_3d(light = NULL)
# disable lighting entirely
# (equivalent to specifying `light(fill = FALSE, color = FALSE`))
p + coord_3d(light = NULL)
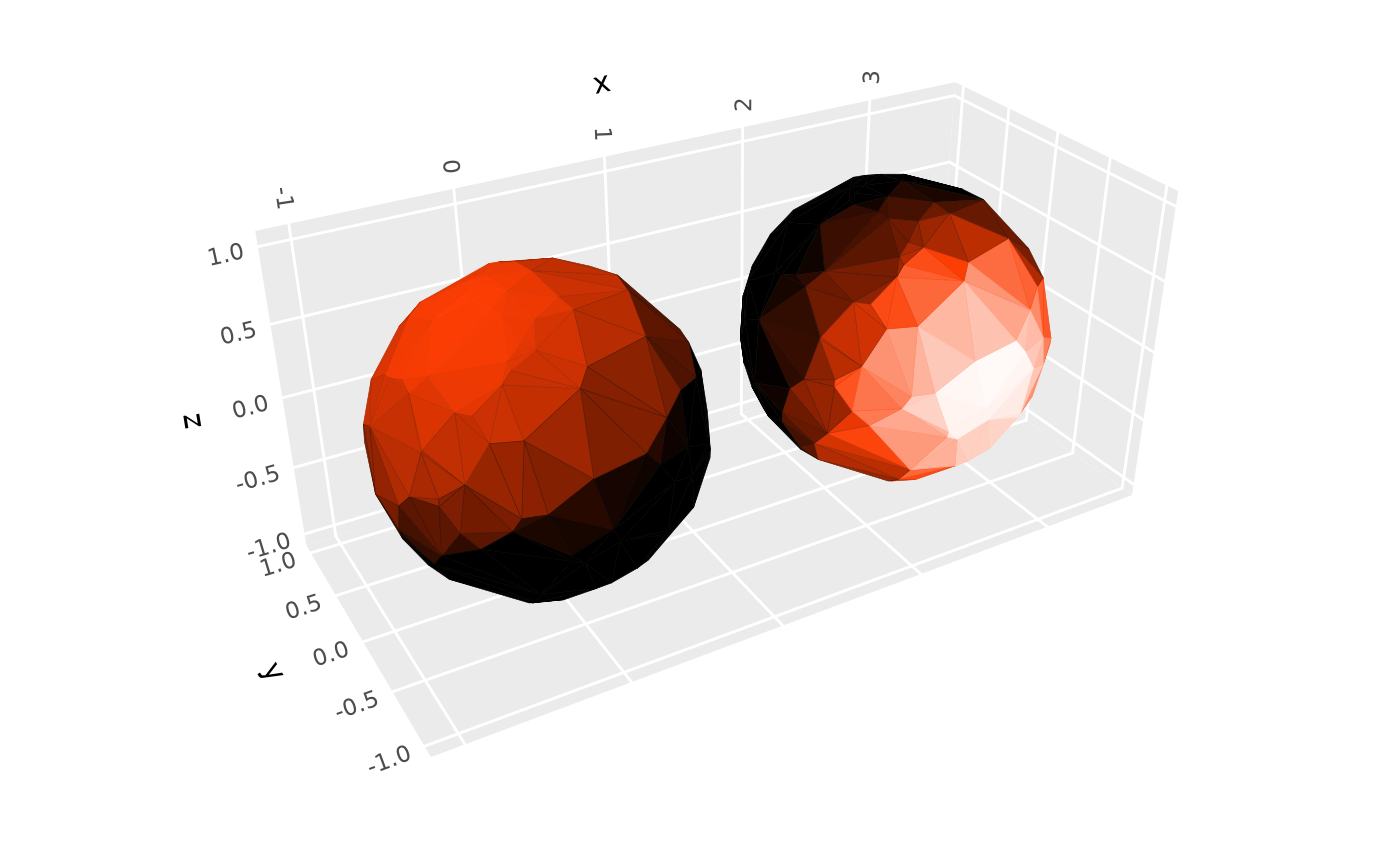
 # if provided, layer-level lighting overrides plot-level (coord_3d) lighting
p + coord_3d(light = light("direct"), # plot-level: affects original layer
scales = "fixed") +
geom_hull_3d(aes(x = x + 2.5), fill = "#9e2602", color = "#5e1600",
light = light("direct", mode = "hsl", direction = c(0, -1, 0)))
# if provided, layer-level lighting overrides plot-level (coord_3d) lighting
p + coord_3d(light = light("direct"), # plot-level: affects original layer
scales = "fixed") +
geom_hull_3d(aes(x = x + 2.5), fill = "#9e2602", color = "#5e1600",
light = light("direct", mode = "hsl", direction = c(0, -1, 0)))
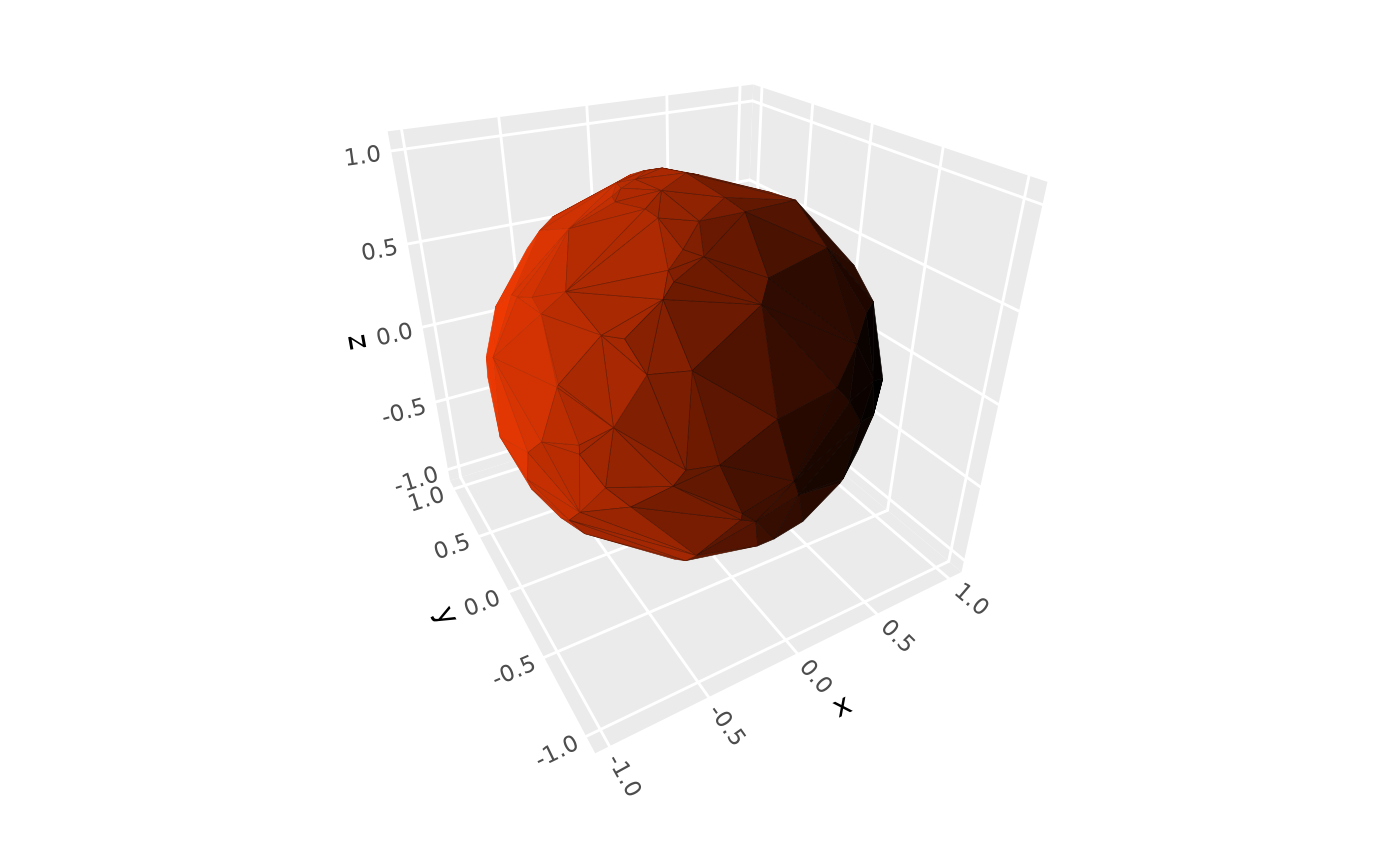
 # Light sources ------------------------------------------------------------
# set directional light as horizontal from back left corner
# (left = negative x, back = positive y, horizontal = neutral z)
p + coord_3d(light = light(direction = c(-1, 1, 0)))
# Light sources ------------------------------------------------------------
# set directional light as horizontal from back left corner
# (left = negative x, back = positive y, horizontal = neutral z)
p + coord_3d(light = light(direction = c(-1, 1, 0)))
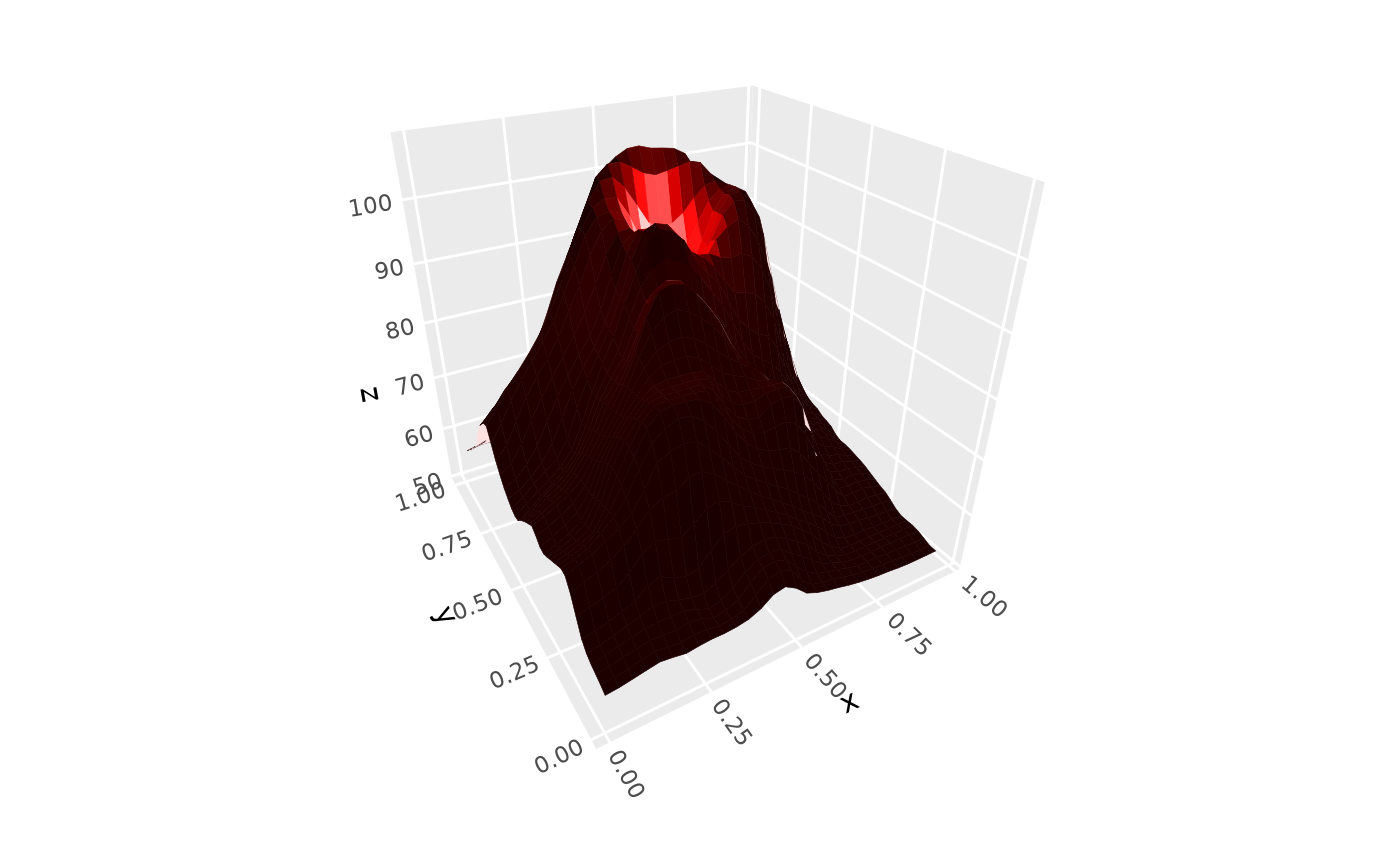
 # specify positional light source within plot
ggplot(mountain, aes(x, y, z)) +
stat_surface_3d(fill = "red", color = "red") +
coord_3d(light = light(position = c(.5, .7, 95),
distance_falloff = TRUE, mode = "hsl", contrast = .9))
# specify positional light source within plot
ggplot(mountain, aes(x, y, z)) +
stat_surface_3d(fill = "red", color = "red") +
coord_3d(light = light(position = c(.5, .7, 95),
distance_falloff = TRUE, mode = "hsl", contrast = .9))
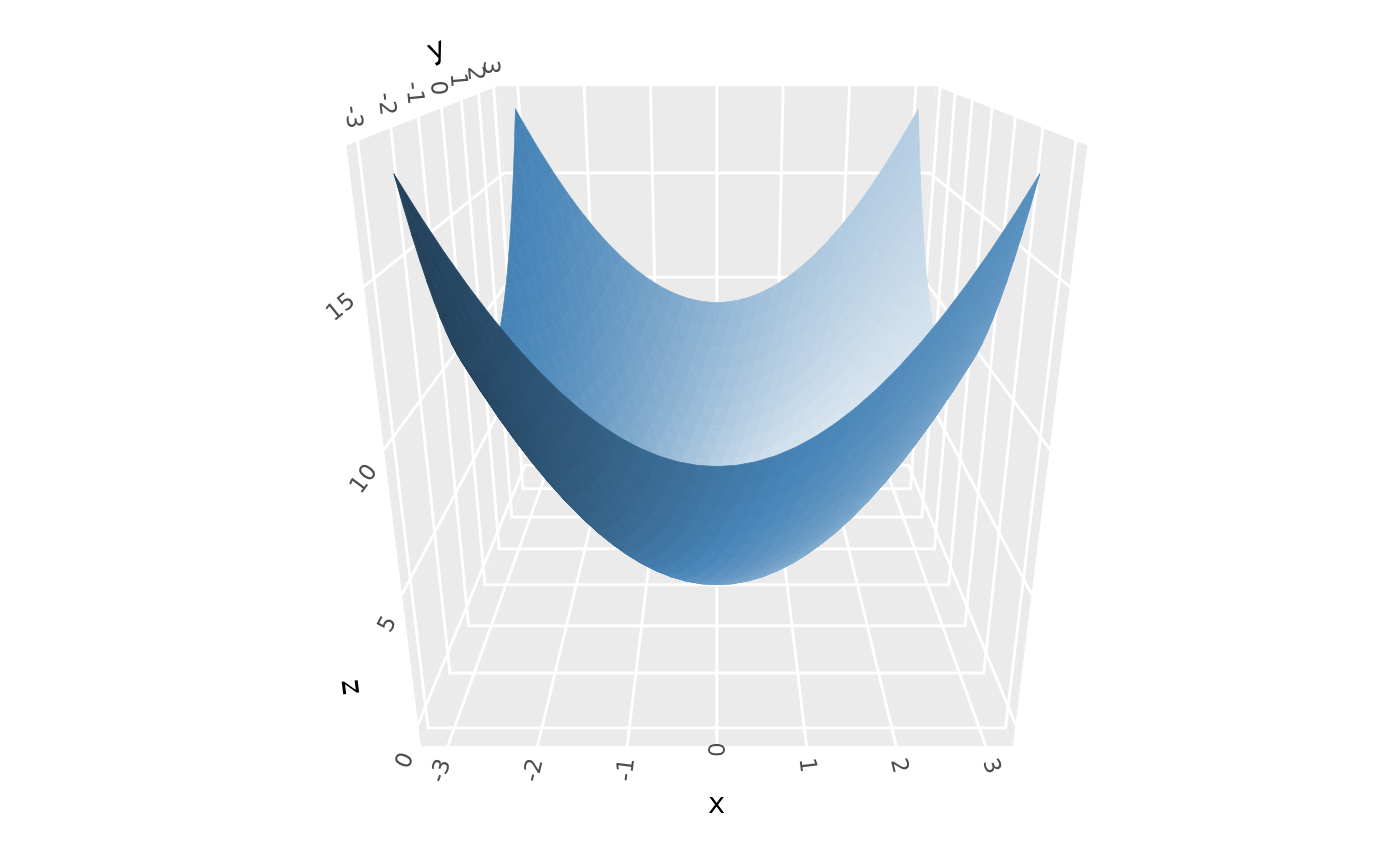
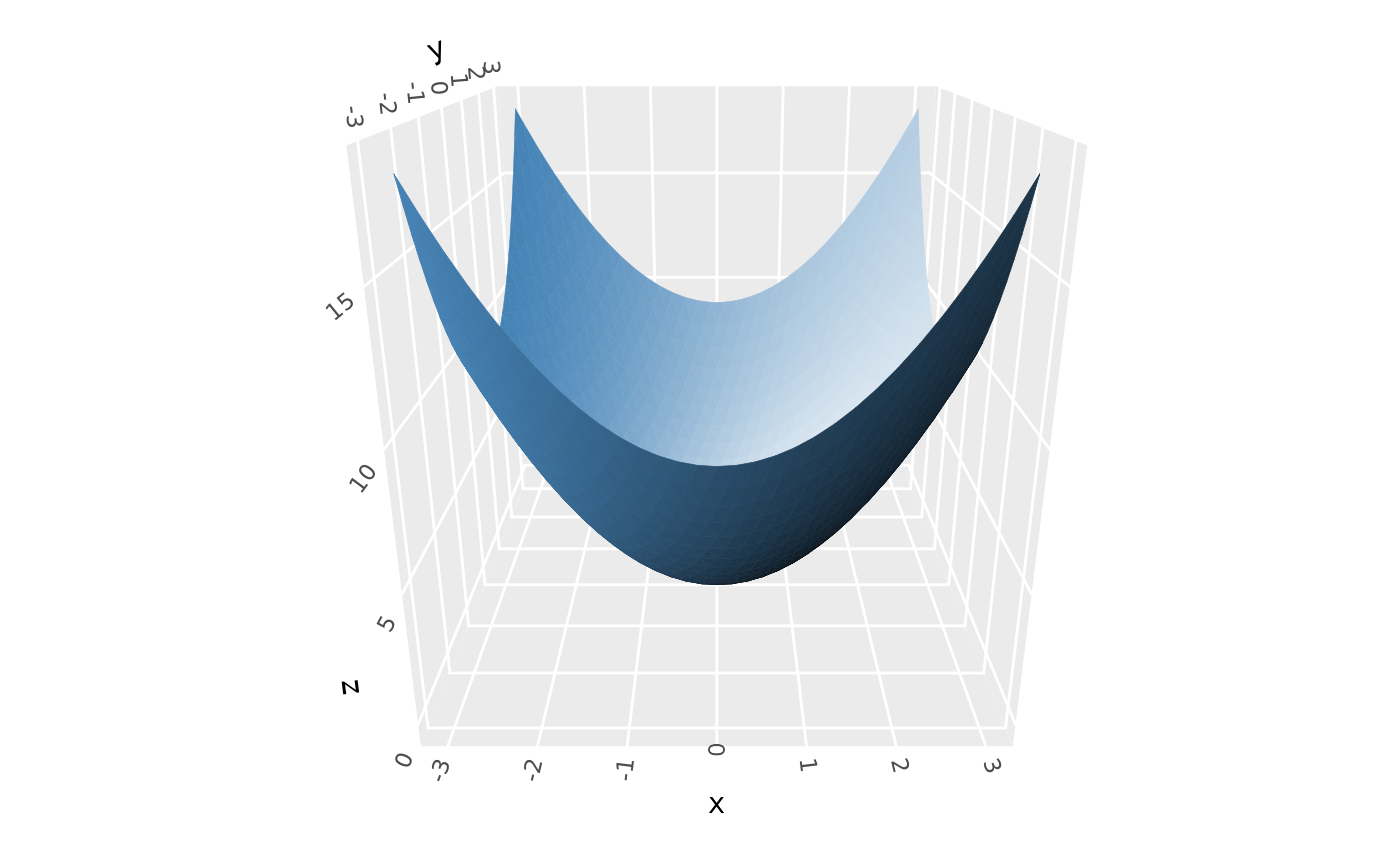
 # Backface lighting --------------------------------------------------------
# backfaces get "opposite" lighting by default (`backface_scale = -1`)
p <- ggplot() +
geom_function_3d(fun = function(x, y) x^2 + y^2,
xlim = c(-3, 3), ylim = c(-3, 3),
fill = "steelblue", color = "steelblue")
p + coord_3d(pitch = 0, roll = -70, yaw = 0,
light = light(mode = "hsl"))
# Backface lighting --------------------------------------------------------
# backfaces get "opposite" lighting by default (`backface_scale = -1`)
p <- ggplot() +
geom_function_3d(fun = function(x, y) x^2 + y^2,
xlim = c(-3, 3), ylim = c(-3, 3),
fill = "steelblue", color = "steelblue")
p + coord_3d(pitch = 0, roll = -70, yaw = 0,
light = light(mode = "hsl"))
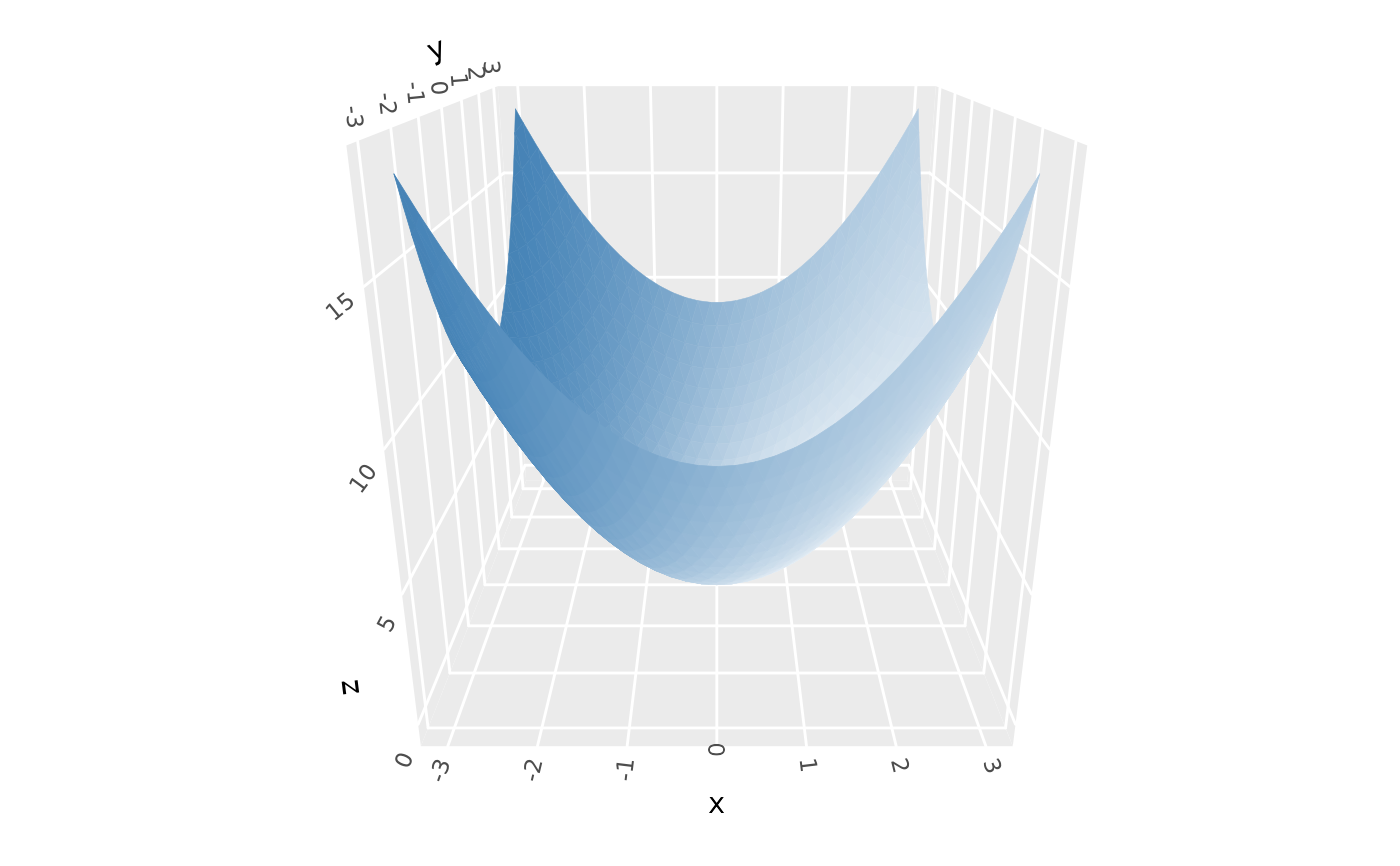
 # use `backface_scale = 1` to light backfaces as if they're frontfaces
p + coord_3d(pitch = 0, roll = -70, yaw = 0,
light = light(backface_scale = 1, mode = "hsl"))
# use `backface_scale = 1` to light backfaces as if they're frontfaces
p + coord_3d(pitch = 0, roll = -70, yaw = 0,
light = light(backface_scale = 1, mode = "hsl"))
 # use `backface_offset` to uniformly darken (or lighten) backfaces
p + coord_3d(pitch = 0, roll = -70, yaw = 0,
light = light(backface_scale = 1, mode = "hsl",
backface_offset = -.5))
# use `backface_offset` to uniformly darken (or lighten) backfaces
p + coord_3d(pitch = 0, roll = -70, yaw = 0,
light = light(backface_scale = 1, mode = "hsl",
backface_offset = -.5))