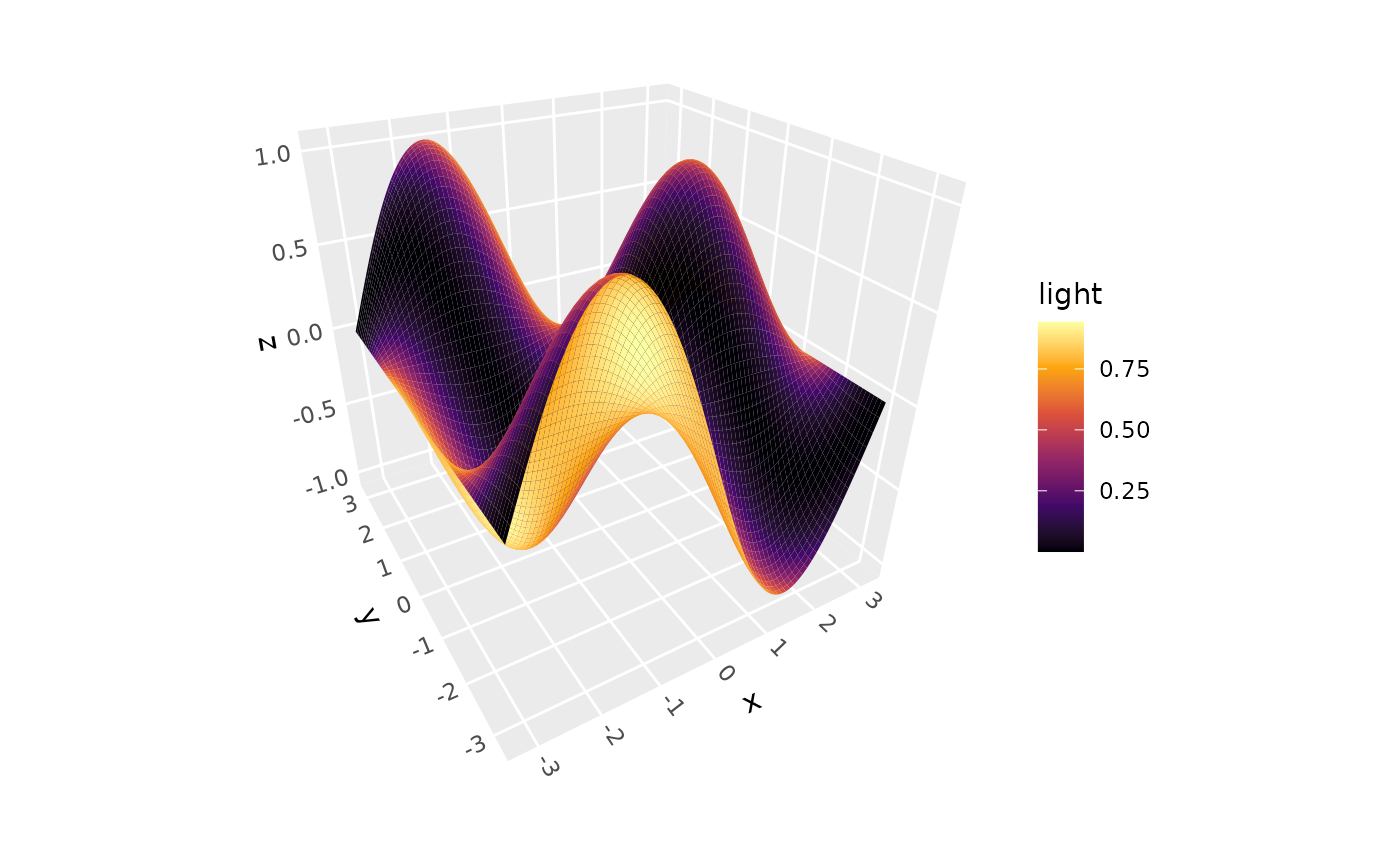
Evaluates a function f(x,y) = z over a regular grid and renders the result as a 3D surface or ridgeline plot.
Usage
stat_function_3d(
mapping = NULL,
data = ensure_nonempty_data,
geom = "surface_3d",
position = "identity",
...,
fun = NULL,
xlim = NULL,
ylim = NULL,
n = 40,
cull_backfaces = FALSE,
light = NULL,
na.rm = FALSE,
show.legend = NA,
inherit.aes = TRUE
)
geom_function_3d(
mapping = NULL,
data = ensure_nonempty_data,
stat = "function_3d",
position = "identity",
...,
fun = NULL,
xlim = NULL,
ylim = NULL,
n = 40,
cull_backfaces = FALSE,
light = NULL,
na.rm = FALSE,
show.legend = NA,
inherit.aes = TRUE
)Arguments
- mapping
Set of aesthetic mappings created by
aes().- data
Ignored; this stat generates its own data.
- geom
Geom to use for rendering. Defaults to GeomSurface3D for mesh surfaces. Use GeomRidgeline3D for ridgeline rendering.
- position
Position adjustment, defaults to "identity".
- ...
Other arguments passed to the layer.
- fun
Function to evaluate. Must accept (x, y) and return numeric z values.
- light
A lighting specification object created by
light(),"none"to disable lighting, orNULLto inherit plot-level lighting specs from the coord. Specify plot-level lighting incoord_3d()and layer-specific lighting ingeom_*3d()functions.- na.rm
If
FALSE, missing values are removed.- show.legend
Logical indicating whether this layer should be included in legends.
- inherit.aes
If
FALSE, overrides the default aesthetics.
Computed variables
- x, y, z
Grid coordinates and function values
- dzdx, dzdy
Partial derivatives at each point
- slope
Gradient magnitude: sqrt(dzdx^2 + dzdy^2)
- aspect
Direction of steepest slope: atan2(dzdy, dzdx)
Examples
# Basic function surface
ggplot() +
geom_function_3d(fun = function(x, y) sin(x) * cos(y),
xlim = c(-pi, pi), ylim = c(-pi, pi)) +
coord_3d()
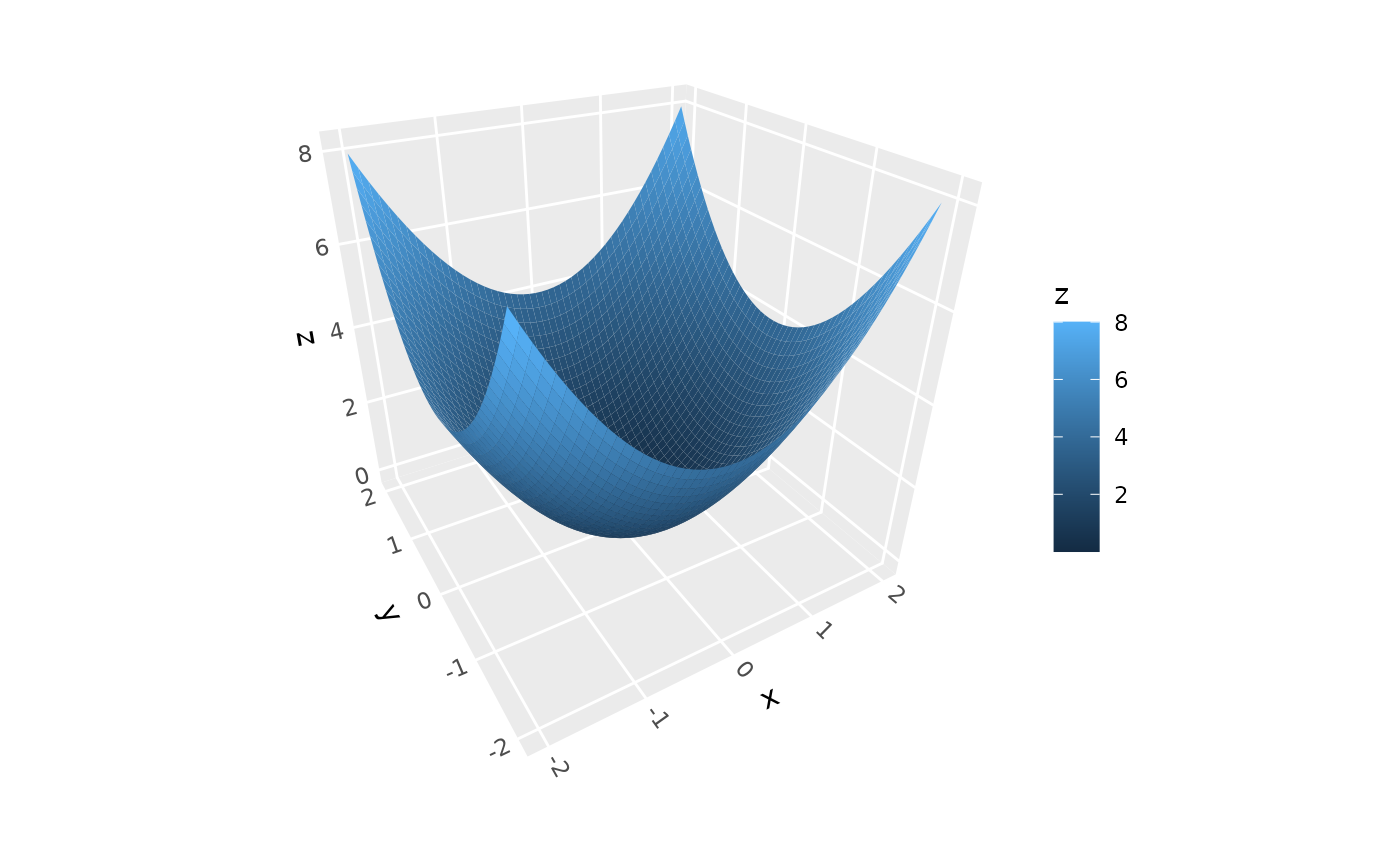 # Fill by slope
ggplot() +
geom_function_3d(fun = function(x, y) x^2 + y^2,
xlim = c(-2, 2), ylim = c(-2, 2),
aes(fill = after_stat(slope))) +
scale_fill_viridis_c() +
coord_3d()
# Fill by slope
ggplot() +
geom_function_3d(fun = function(x, y) x^2 + y^2,
xlim = c(-2, 2), ylim = c(-2, 2),
aes(fill = after_stat(slope))) +
scale_fill_viridis_c() +
coord_3d()
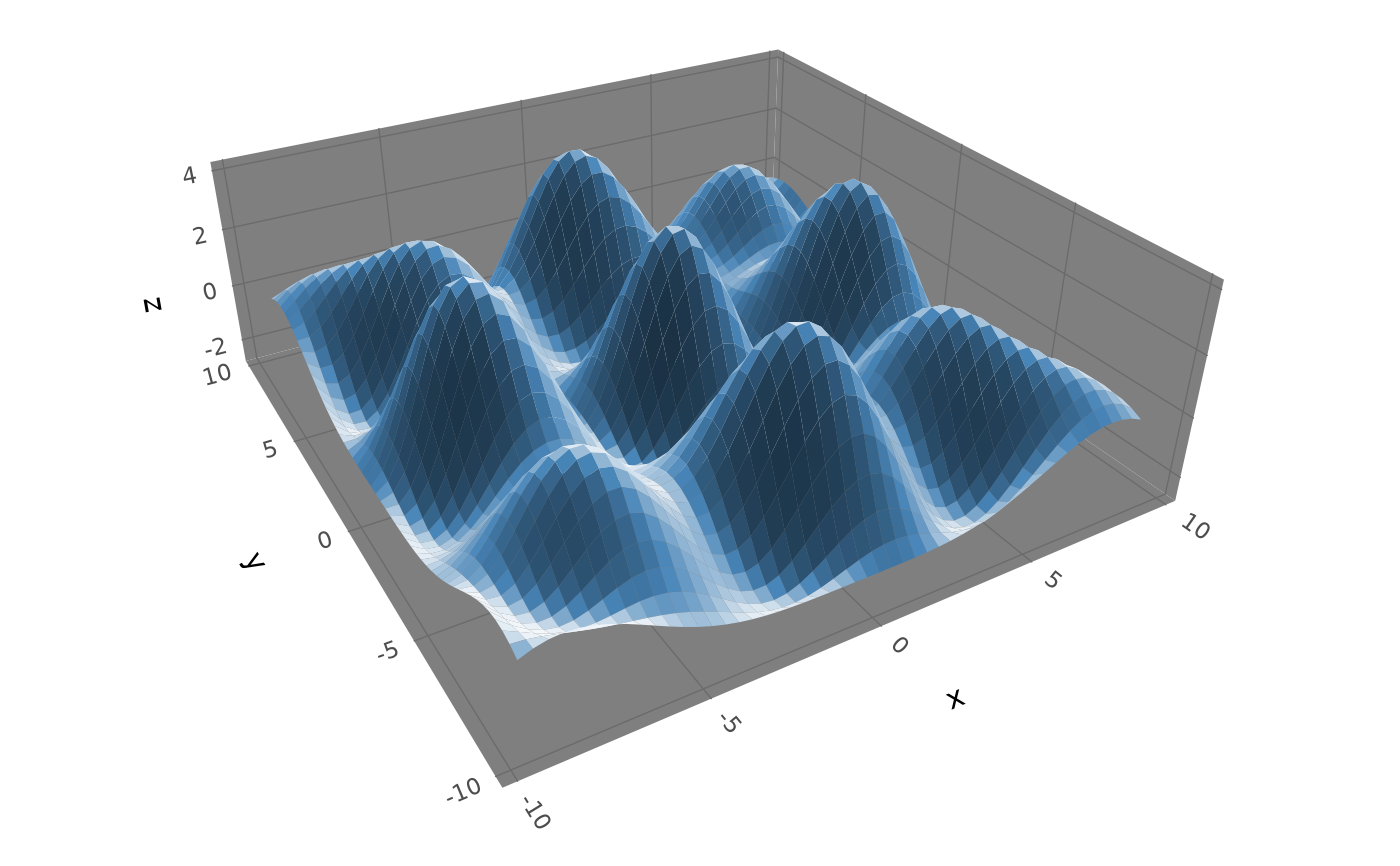 # As ridgelines
ggplot() +
stat_function_3d(fun = function(x, y) dnorm(x) * dnorm(y) * 10,
xlim = c(-1.5, 1.5), ylim = c(-1.5, 1.5), n = c(15, 30),
geom = "ridgeline_3d", base = 0, light = "none",
fill = "black", color = "white") +
coord_3d()
# As ridgelines
ggplot() +
stat_function_3d(fun = function(x, y) dnorm(x) * dnorm(y) * 10,
xlim = c(-1.5, 1.5), ylim = c(-1.5, 1.5), n = c(15, 30),
geom = "ridgeline_3d", base = 0, light = "none",
fill = "black", color = "white") +
coord_3d()