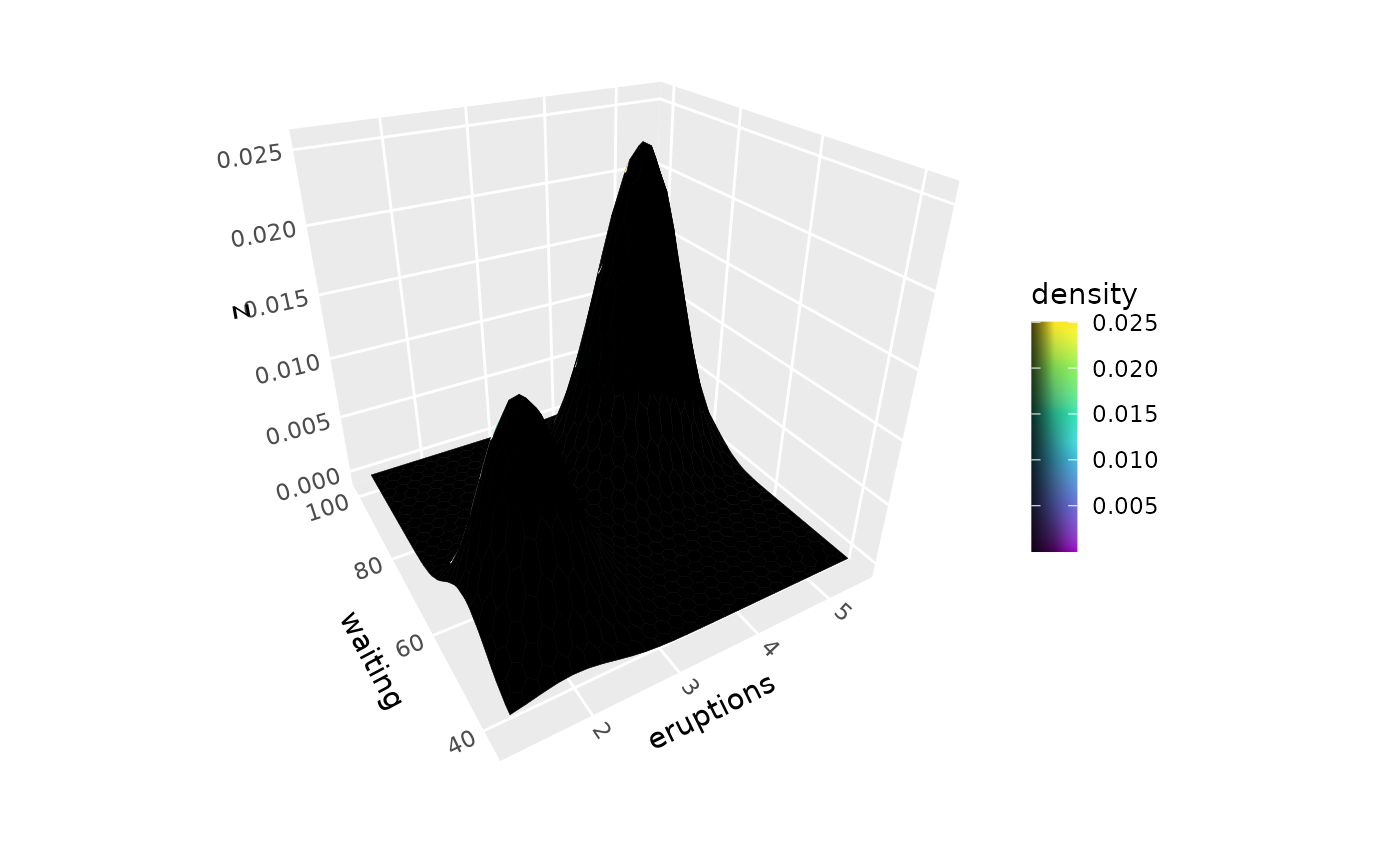
A 3D version of ggplot2::geom_density_2d().
Creates surfaces from 2D point data using kernel density estimation.
The density values become the z-coordinates of the surface, allowing
visualization of data concentration as peaks and valleys in 3D space.
Usage
geom_density_3d(
mapping = NULL,
data = NULL,
stat = StatDensity3D,
position = "identity",
...,
n = NULL,
grid = NULL,
direction = NULL,
trim = NULL,
h = NULL,
adjust = 1,
pad = 0.1,
min_ndensity = 0,
light = NULL,
cull_backfaces = FALSE,
sort_method = NULL,
force_convex = TRUE,
scale_depth = TRUE,
na.rm = FALSE,
show.legend = NA,
inherit.aes = TRUE
)
stat_density_3d(
mapping = NULL,
data = NULL,
geom = GeomPolygon3D,
position = "identity",
...,
n = NULL,
grid = NULL,
direction = NULL,
trim = NULL,
h = NULL,
adjust = 1,
pad = 0.1,
min_ndensity = 0,
light = NULL,
cull_backfaces = FALSE,
sort_method = NULL,
force_convex = TRUE,
scale_depth = TRUE,
na.rm = FALSE,
show.legend = NA,
inherit.aes = TRUE
)Arguments
- mapping
Set of aesthetic mappings created by
aes(). This stat requiresxandyaesthetics. By default,fillis mapped toafter_stat(density)andzis mapped toafter_stat(density).- data
The data to be displayed in this layer. Must contain x and y columns with point coordinates.
- stat
The statistical transformation to use on the data. Defaults to
StatDensity3D.- position
Position adjustment, defaults to "identity". To collapse the result onto one 2D surface, use
position_on_face().- ...
Other arguments passed on to the the layer function (typically GeomPolygon3D), such as aesthetics like
colour,fill,linewidth, etc.- grid, n, direction, trim
Parameters determining the geometry, resolution, and orientation of the surface grid. See grid_generation for details.
- h
Bandwidth vector. If
NULL(default), uses automatic bandwidth selection viaMASS::bandwidth.nrd(). Can be a single number (used for both dimensions) or a vector of length 2 for different bandwidths in x and y directions.- adjust
Multiplicative bandwidth adjustment factor. Values greater than 1 produce smoother surfaces; values less than 1 produce more detailed surfaces. Default is 1.
- pad
Proportional range expansion factor. The computed density grid extends this proportion of the raw data range beyond each data limit. Default is 0.1.
- min_ndensity
Lower cutoff for normalized density (computed variable
ndensitydescribed below), below which to filter out results. This is particularly useful for removing low-density corners of rectangular density grids when density surfaces are shown for multiple groups, as in the example below. Default is 0 (no filtering).- light
A lighting specification object created by
light()(see that function for details), orNULLto disable shading. Specify plot-level lighting incoord_3d()and layer-specific lighting ingeom_*3d()functions.- cull_backfaces, sort_method, force_convex, scale_depth
Advanced polygon rendering parameters. See polygon_rendering for details.
- na.rm
If
FALSE, missing values are removed.- show.legend
Logical indicating whether this layer should be included in legends.
- inherit.aes
If
FALSE, overrides the default aesthetics.- geom
The geometric object used to display the data. Defaults to
GeomPolygon3D.
Aesthetics
stat_density_3d() requires the following aesthetics from input data:
x: X coordinate of data points
y: Y coordinate of data points
And optionally understands:
group: Grouping variable for computing separate density surfaces
Additional aesthetics are passed through for surface styling
Computed variables specific to StatDensity3D
density: The kernel density estimate at each grid pointndensity: Density estimate scaled to maximum of 1 within each groupcount: Density estimate × number of observations in group (expected count)n: Number of observations in each group
Grouping
When aesthetics like colour or fill are mapped to categorical variables,
stat_density_3d() computes separate density surfaces for each group, just
like stat_density_2d(). Each group gets its own density calculation with
proper count and n values.
Computed variables
The following computed variables are available via after_stat():
x,y,z: Grid coordinates and function valuesnormal_x,normal_y,normal_z: Surface normal componentsslope: Gradient magnitude from surface calculationsaspect: Direction of steepest slope from surface calculationsdzdx,dzdy: Partial derivatives from surface calculation
See also
stat_density_2d() for 2D density contours, stat_surface_3d() for
surfaces from existing grid data, light() for lighting specifications,
make_tile_grid() for details about grid geometry options,
coord_3d() for 3D coordinate systems.
Examples
library(ggplot2)
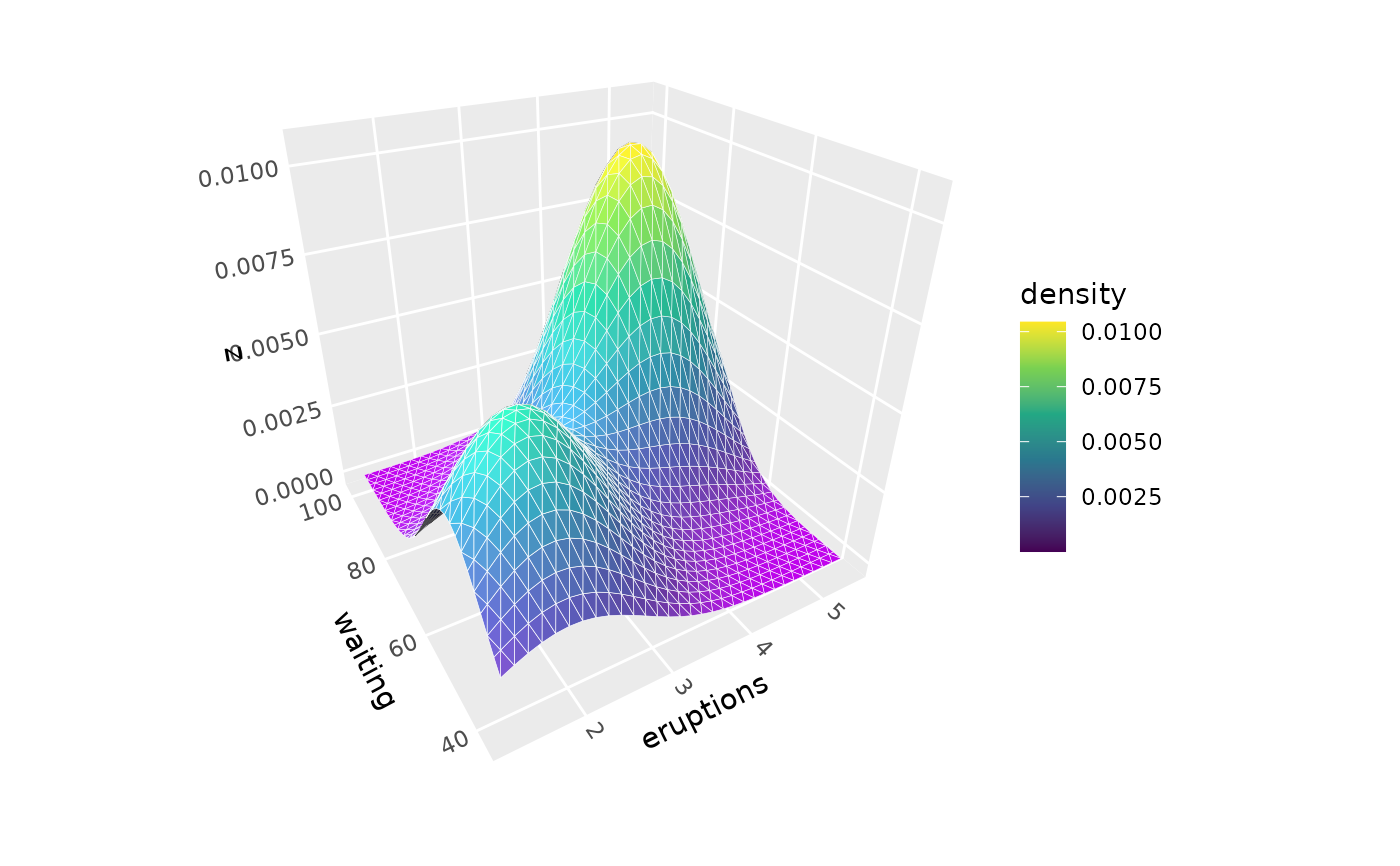
# Basic density surface from scattered points
p <- ggplot(faithful, aes(eruptions, waiting)) +
coord_3d() +
scale_fill_viridis_c()
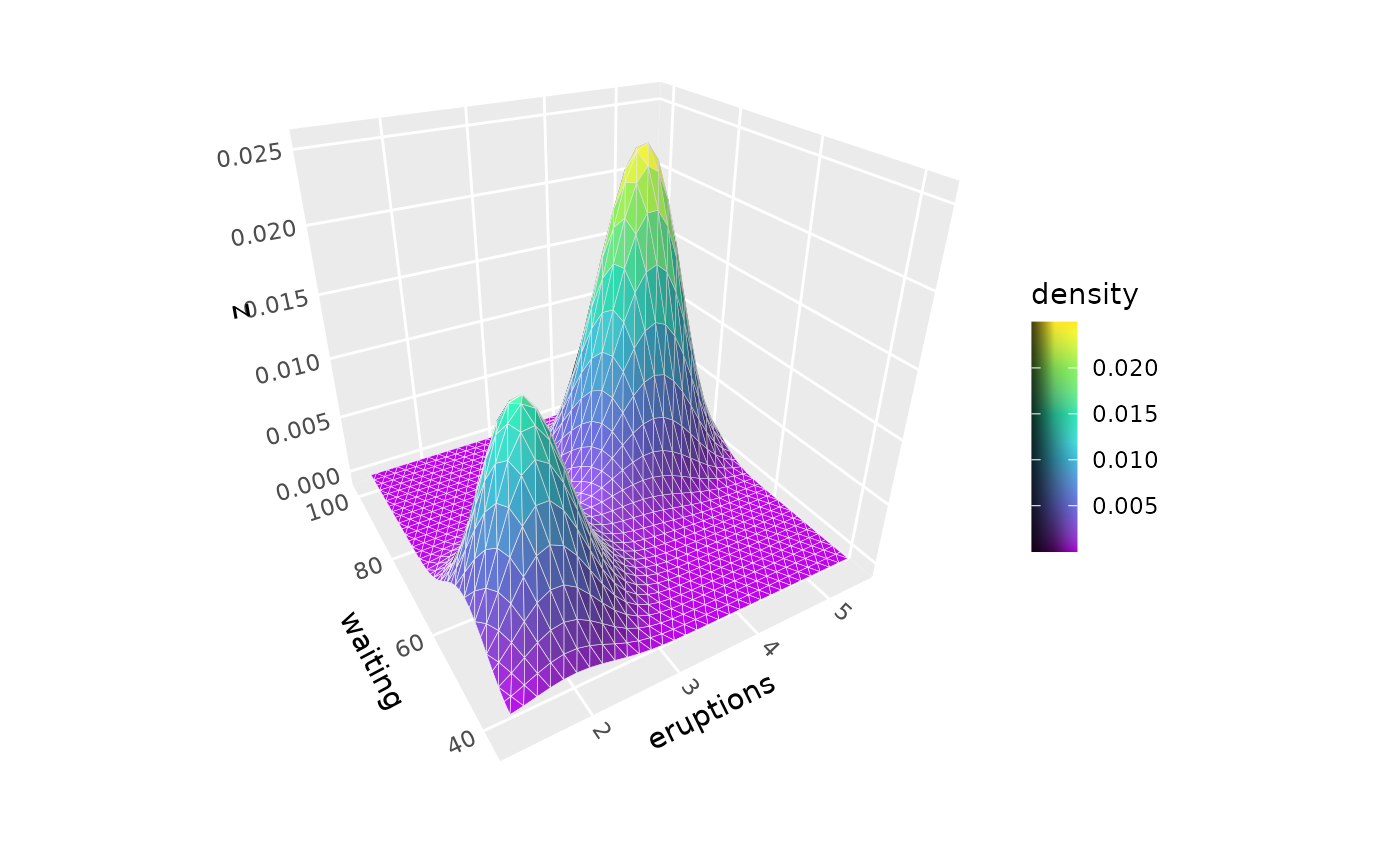
p + geom_density_3d() + guides(fill = guide_colorbar_3d())
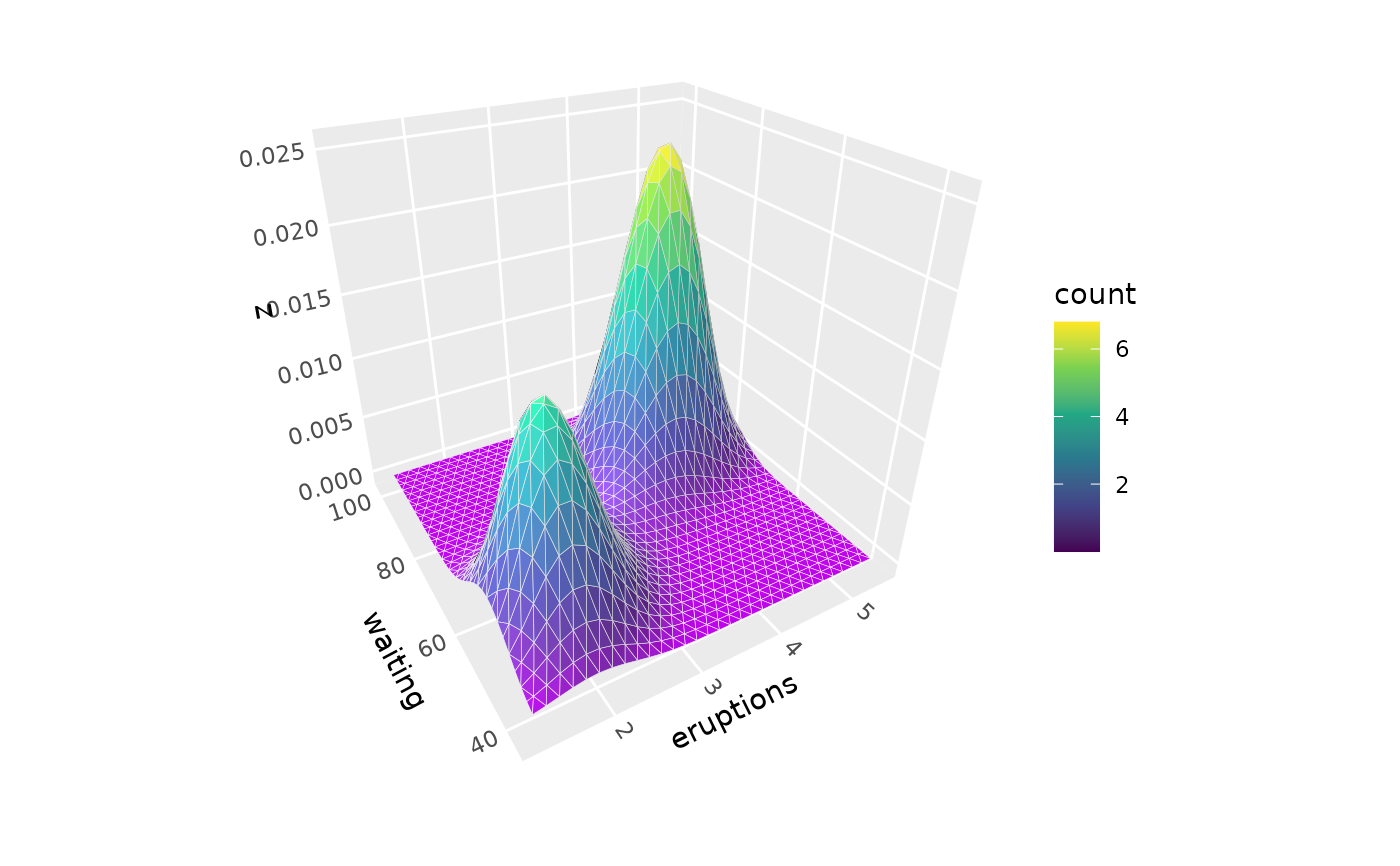
 # Color by alternative density values
p + geom_density_3d(aes(fill = after_stat(count)))
# Color by alternative density values
p + geom_density_3d(aes(fill = after_stat(count)))
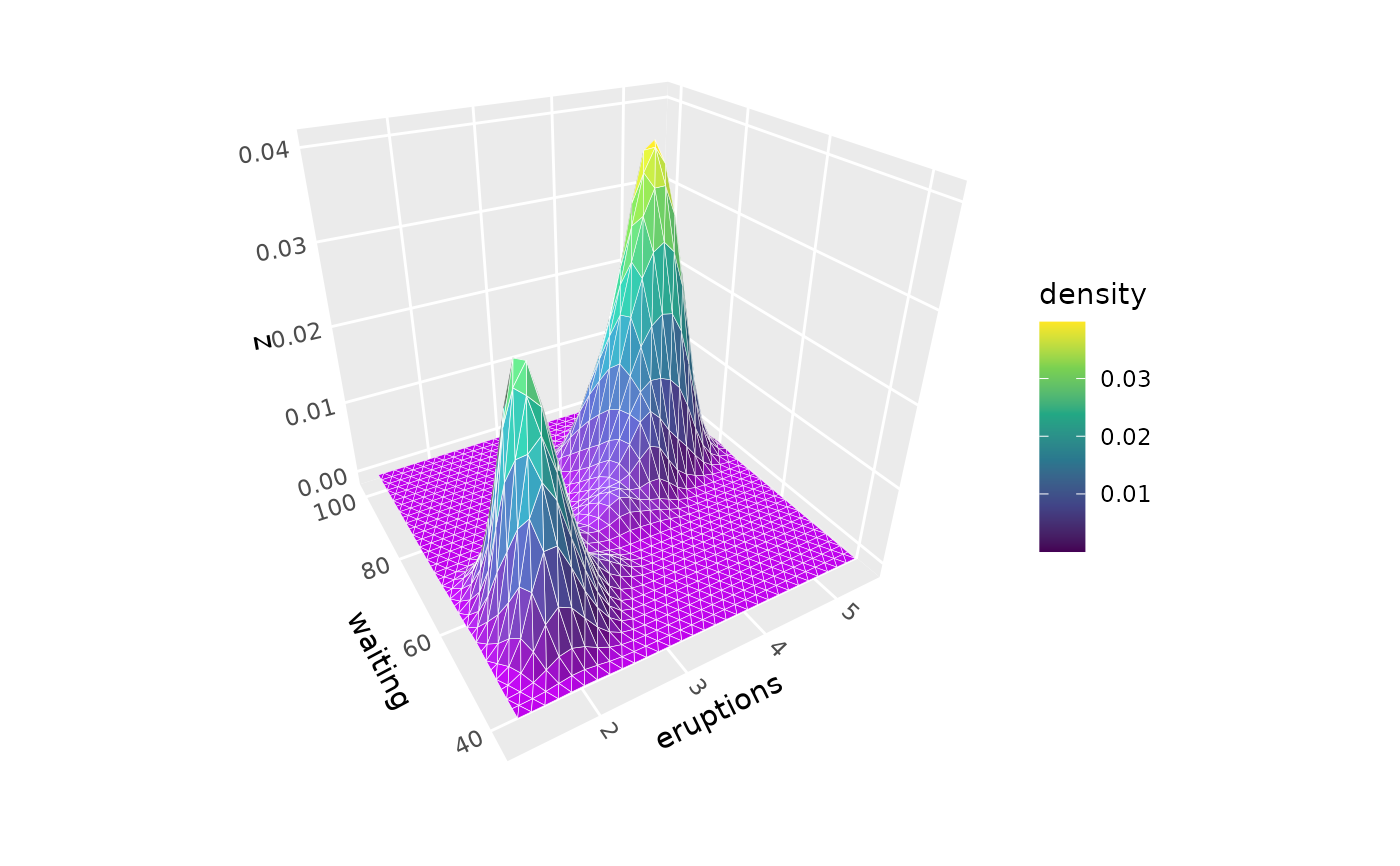
 # Adjust bandwidth for smoother or more detailed surfaces
p + geom_density_3d(adjust = 0.5, color = "white") # More detail
# Adjust bandwidth for smoother or more detailed surfaces
p + geom_density_3d(adjust = 0.5, color = "white") # More detail
 p + geom_density_3d(adjust = 2, color = "white") # Smoother
p + geom_density_3d(adjust = 2, color = "white") # Smoother
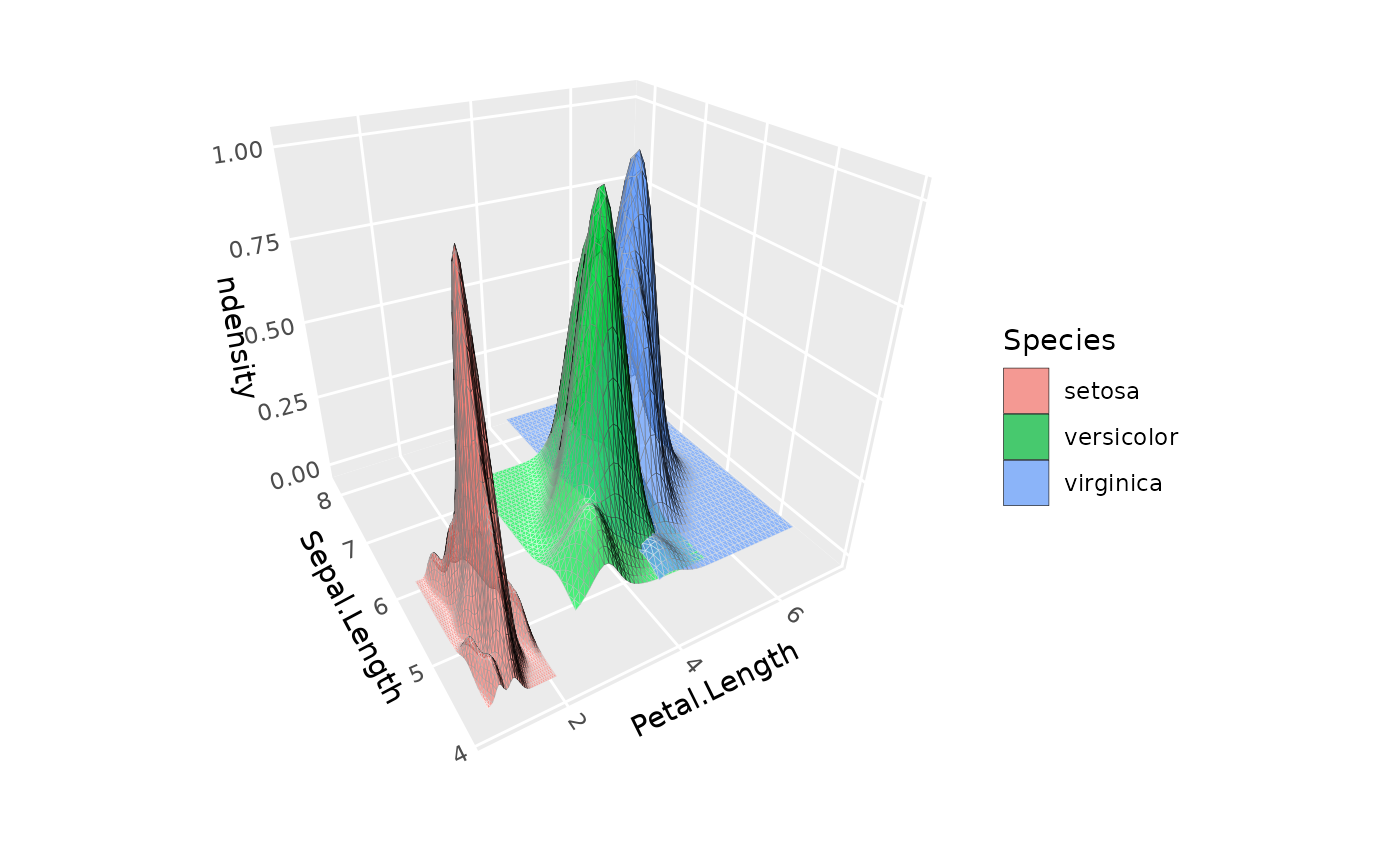
 # Multiple density surfaces by group,
# using normalized density to equalize peak heights
ggplot(iris, aes(Petal.Length, Sepal.Length, fill = Species)) +
geom_density_3d(aes(z = after_stat(ndensity), group = Species),
color = "black", alpha = .7, light = NULL) +
coord_3d()
# Multiple density surfaces by group,
# using normalized density to equalize peak heights
ggplot(iris, aes(Petal.Length, Sepal.Length, fill = Species)) +
geom_density_3d(aes(z = after_stat(ndensity), group = Species),
color = "black", alpha = .7, light = NULL) +
coord_3d()
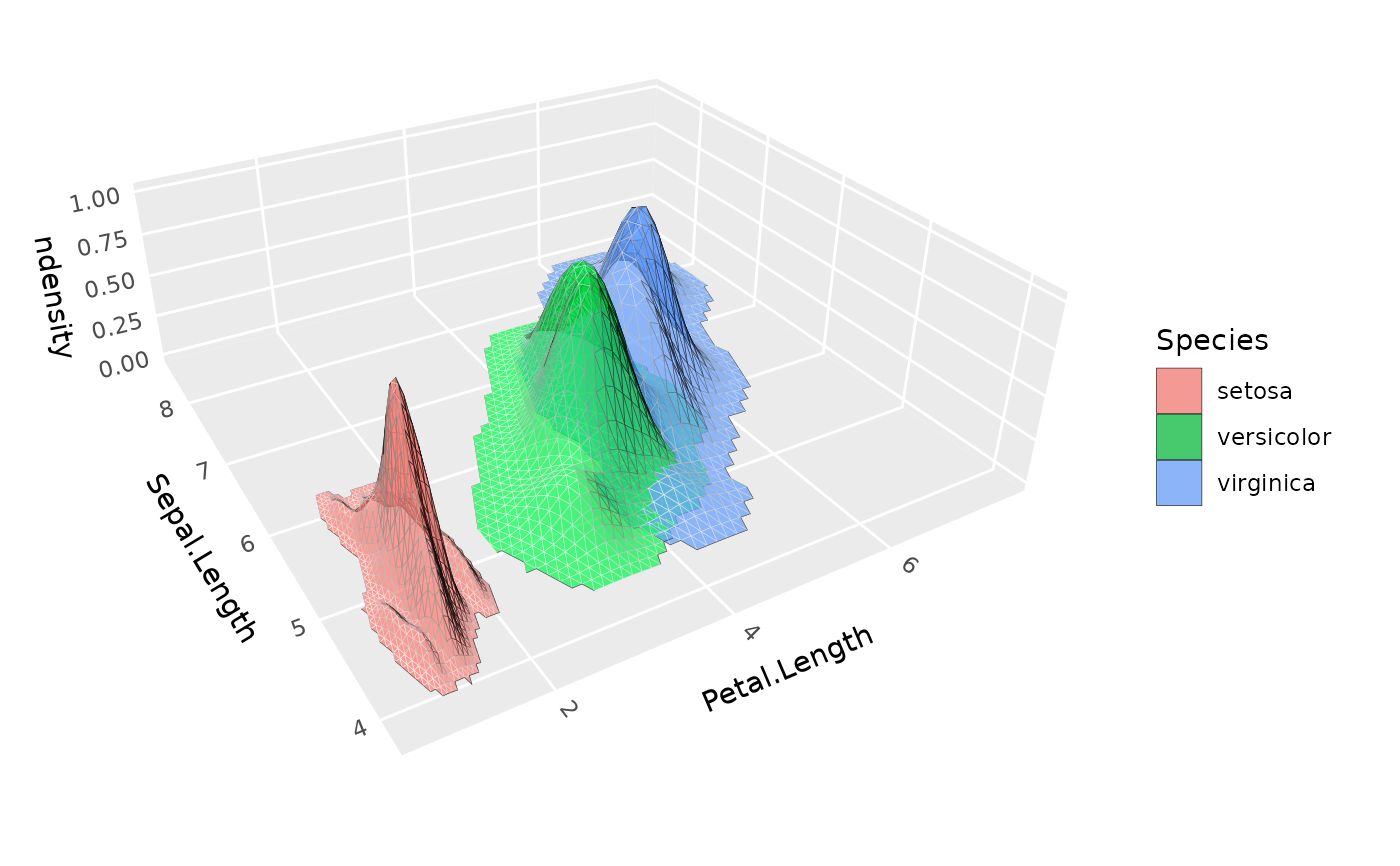
 # Same, but with extra padding to remove edge effects and
# with density filtering to remove rectangular artifacts
ggplot(iris, aes(Petal.Length, Sepal.Length, fill = Species)) +
geom_density_3d(aes(z = after_stat(ndensity)),
pad = .3, min_ndensity = .001,
color = "black", alpha = .7, light = NULL) +
coord_3d(ratio = c(3, 3, 1))
# Same, but with extra padding to remove edge effects and
# with density filtering to remove rectangular artifacts
ggplot(iris, aes(Petal.Length, Sepal.Length, fill = Species)) +
geom_density_3d(aes(z = after_stat(ndensity)),
pad = .3, min_ndensity = .001,
color = "black", alpha = .7, light = NULL) +
coord_3d(ratio = c(3, 3, 1))
 # Specify alternative grid geometry and light model
p + geom_density_3d(grid = "hex", n = 30, direction = "y",
light = light("direct"),
color = "white", linewidth = .1) +
guides(fill = guide_colorbar_3d())
# Specify alternative grid geometry and light model
p + geom_density_3d(grid = "hex", n = 30, direction = "y",
light = light("direct"),
color = "white", linewidth = .1) +
guides(fill = guide_colorbar_3d())