Perform a clustering analysis that categorizes sites into biogeographic regions based on phylogenetic community compositional similarity.
Arguments
- ps
A
phylospatialobject. Ifmethodis anything other than"kmeans", it must contain adissimcomponent generated by ps_add_dissim.- k
Number of spatial clusters to divide the region into (positive integer). See ps_regions_eval to help choose a value of k by comparing the variance explained by different numbers of regions.
- method
Clustering method. Options include all methods listed under hclust, and
"kmeans". If"kmeans"is selected, thedissimcomponent ofpsis ignored.- endemism
Logical indicating whether community values should be divided by column totals (taxon range sizes) to derive endemism. Only used if
method = "kmeans"; in other cases this information should instead be supplied to ps_add_dissim.- normalize
Logical indicating whether community values should be divided by row totals (community sums). If
TRUE, dissimilarity is based on proportional community composition. This happens after endemism is derived. Only used ifmethod = "kmeans"; in other cases this information should instead be supplied to ps_add_dissim.
References
Daru, B. H., Elliott, T. L., Park, D. S., & Davies, T. J. (2017). Understanding the processes underpinning patterns of phylogenetic regionalization. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 32(11), 845-860.
Examples
ps <- ps_simulate()
# using kmeans clustering algorithm
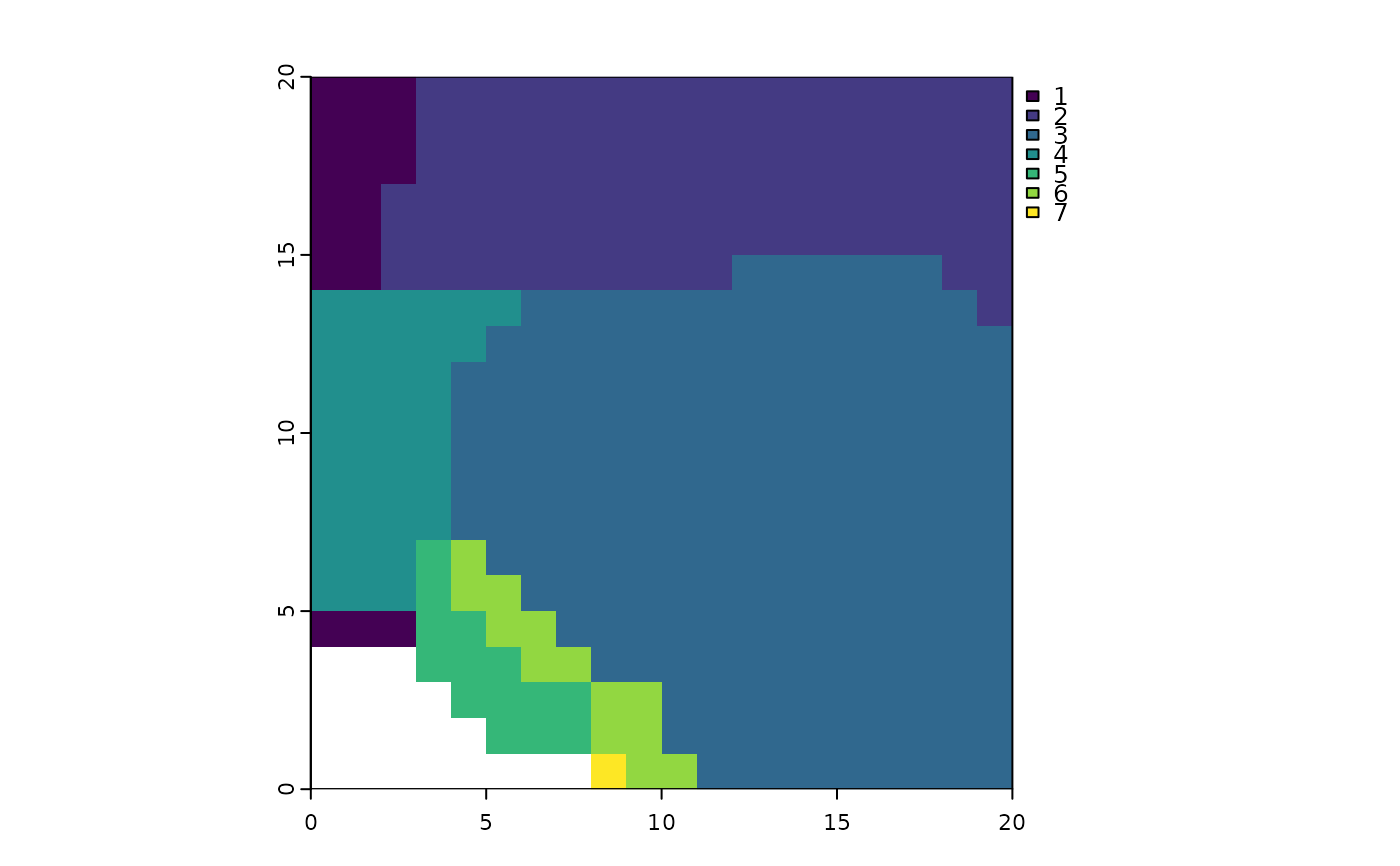
terra::plot(ps_regions(ps, method = "kmeans"))
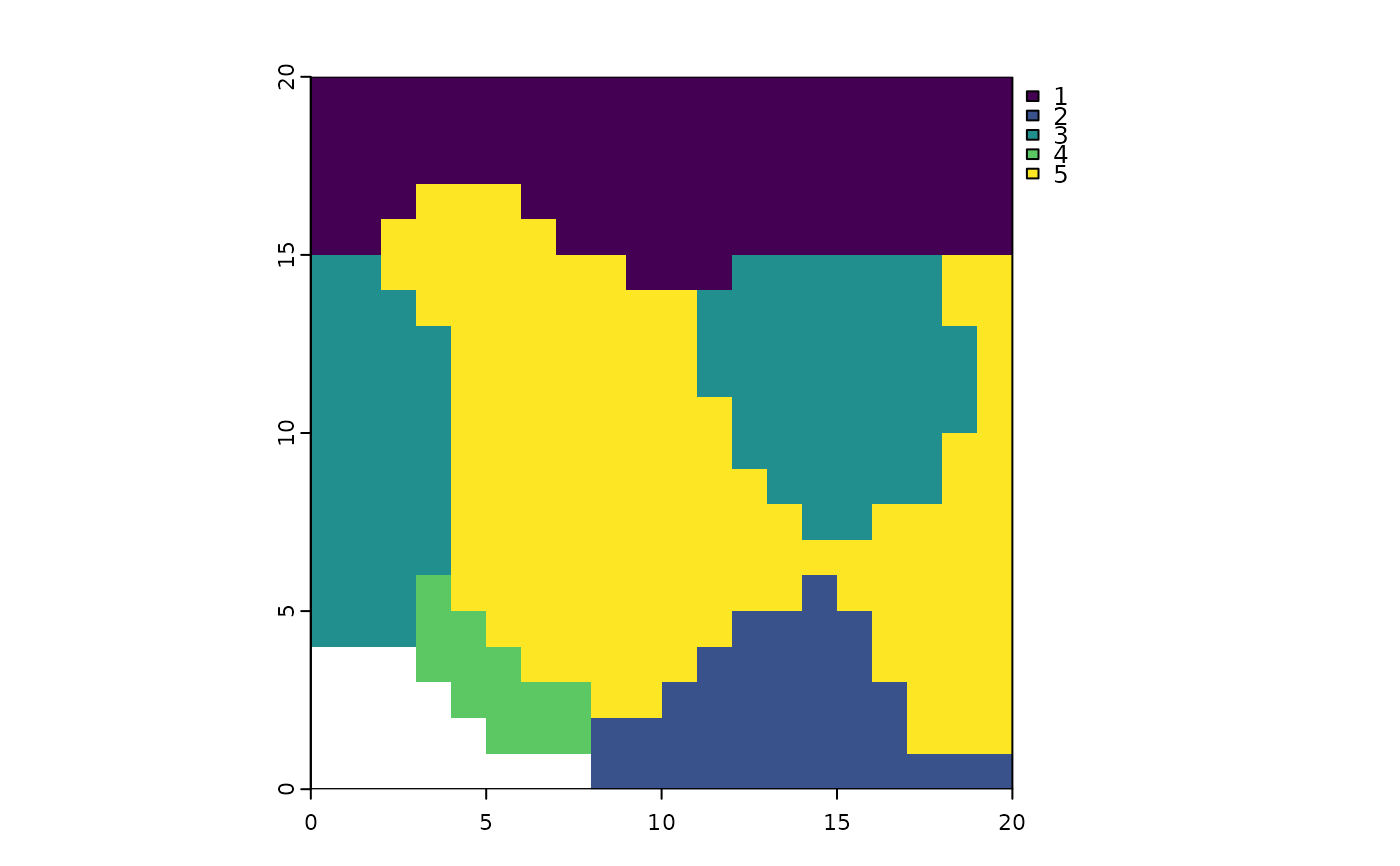 # to use a hierarchical clustering method, first we have to `ps_add_dissim()`
terra::plot(ps_regions(ps_add_dissim(ps), k = 7, method = "average"))
# to use a hierarchical clustering method, first we have to `ps_add_dissim()`
terra::plot(ps_regions(ps_add_dissim(ps), k = 7, method = "average"))