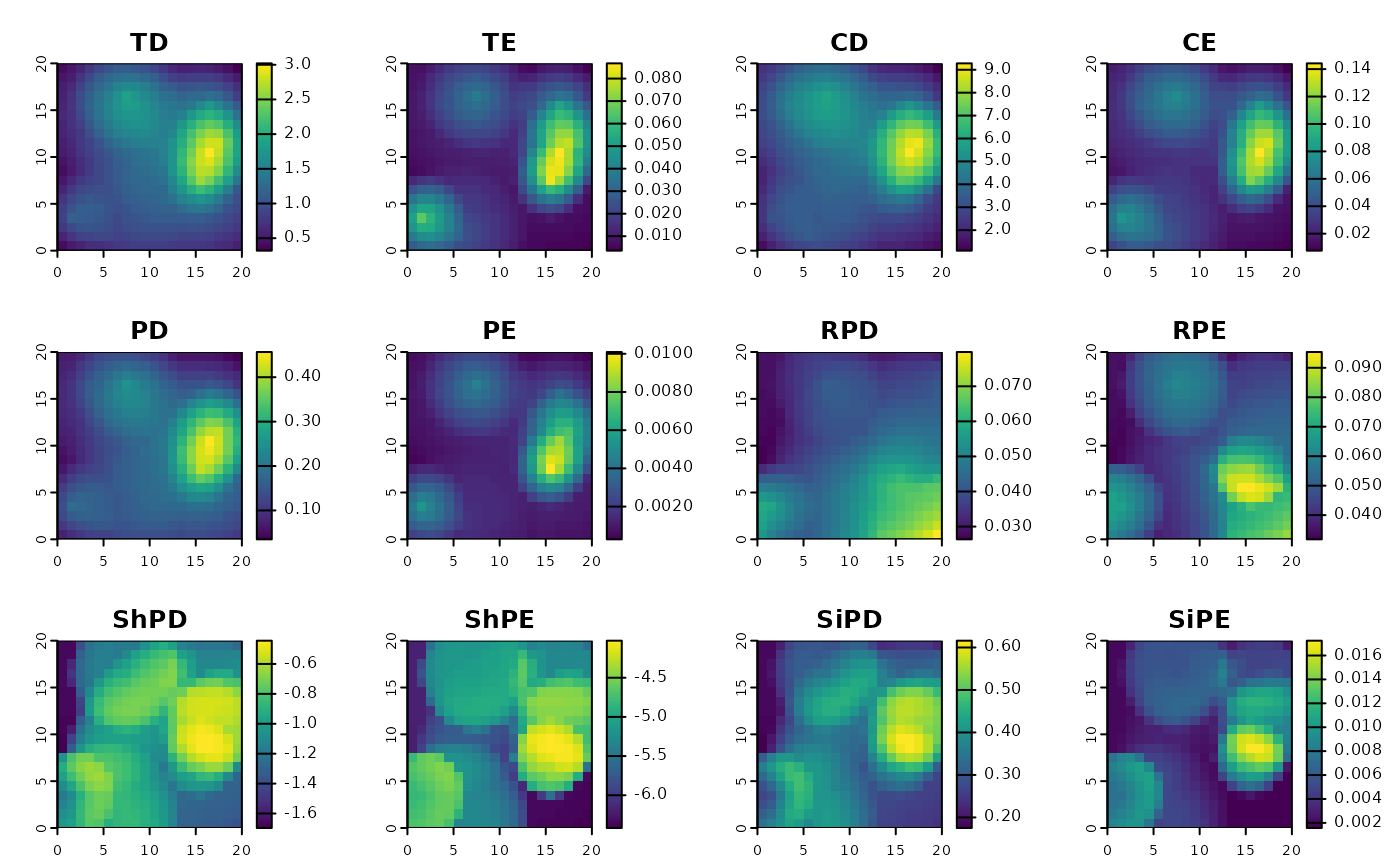
Calculate spatial phylogenetic diversity and endemism metrics
Source:R/ps_diversity.R
ps_diversity.RdThis function calculates a variety of alpha phylogenetic diversity metrics, including measures of richness, regularity, and divergence. If continuous community data (probabilities or abundances) are provided, they are used in calculations, giving quantitative versions of the classic binary metrics.
Usage
ps_diversity(ps, metric = c("PD", "PE", "CE", "RPE"), spatial = TRUE)Arguments
- ps
phylospatial object (created by
phylospatial()orps_simulate()).- metric
Character vector containing the abbreviation for one or more diversity metrics listed in the details below. Can also specify
"all"to calculate all available metrics. A small subset of common measures are selected by default.- spatial
Logical: should the function return a spatial object (TRUE, default) or a matrix (FALSE)?
Value
A matrix, sf data frame, or SpatRaster with a column or layer for each requested diversity metric.
Details
The function calculates the following metrics. Endemism-weighted versions of most metrics are available. All metrics are weighted by occurrence probability or abundance, if applicable.
Richness measures:
TD—Terminal Diversity, i.e. richness of terminal taxa (in many cases these are species): \(\sum_{t}{p_t}\)
TE—Terminal Endemism, i.e. total endemism-weighted diversity of terminal taxa, a.k.a. "weighted endemism": \(\sum_{t}{p_t r_t^{-1}}\)
CD—Clade Diversity, i.e. richness of taxa at all levels (equivalent to PD on a cladogram): \(\sum_{b}{p_b}\)
CE—Clade Endemism, i.e. total endemism-weighted diversity of taxa at all levels (equivalent to PE on a cladrogram): \(\sum_{b}{p_b r_b^{-1}}\)
PD—Phylogenetic Diversity, i.e. total branch length occurring in a site: \(\sum_{b}{L_b p_b}\)
PE—Phylogenetic Endemism, i.e. endemism-weighted PD: \(\sum_{b}{L_b p_b r_b^{-1}}\)
ShPD—Shannon Phylogenetic Diversity, a.k.a. "phylogenetic entropy" (this version is the log of the "effective diversity" version based on Hill numbers): \(-\sum_{b}{L_b n_b log(n_b)}\)
ShPE—Shannon phylogenetic Endemism, an endemism-weighted version of ShPD: \(-\sum_{b}{L_b n_b log(e_b) r_b^{-1}}\)
SiPD—Simpson Phylogenetic Diversity: \(1 / \sum_{b}{L_b n_b^2}\)
SiPE—Simpson Phylogenetic Endemism, an endemism-weighted version of SiPD: \(1 / \sum_{b}{L_b r_b^{-1} e_b^2}\)
Divergence measures:
RPD—Relative Phylogenetic Diversity, i.e. mean branch segment length (equivalent to PD / CR): \(\sum_{b}{L_b p_b} / \sum_{b}{p_b}\)
RPE—Relative Phylogenetic Endemism, i.e. mean endemism-weighted branch segment length (equivalent to PE / CE): \(\sum_{b}{L_b p_b r_b^{-1}} / \sum_{b}{p_b r_b^{-1}}\)
MPDT—Mean Pairwise Distance between Terminals, i.e. the classic MPD metric. This is the average of cophenetic distances, weighted by \(p_t\).
MPDN—Mean Pairwise Distance between Nodes, an experimental version of MPD that considers distances between every pair of non-nested clades, putting more weight on deeper branches than does MPDT. This is the mean of distances between all collateral (non-lineal) node pairs including terminal and internal nodes, weighted by \(p_b\).
Note that divergence can also be assessed by using
ps_rand()to run null model analyses of richness measures like PD.
Regularity measures:
VPDT—Variance in Pairwise Distances between Terminals, i.e. the classic VPD metric, weighted by \(p_t\).
VPDN—Variance in Pairwise Distances between Nodes, i.e. MPDN but variance.
In the above equations, \(b\) indexes all taxa including terminals and larger clades; \(t\) indexes terminals only; \(p_i\) is the occurrence value (binary, probability, or abundance) of clade/terminal \(i\) in a given community; \(L_b\) is the length of the phylogenetic branch segment unique to clade \(b\); and \(r_i\) is the sum of \(p_i\) across all sites. For Shannon and Simpson indices, only nonzero elements of \(p_b\) are used, \(n_b = p_b / \sum_{b}{p_b L_b}\), and \(e_b = p_b / \sum_{b}{p_b L_b r_b^{-1}}\).
References
Faith, D. P. (1992). Conservation evaluation and phylogenetic diversity. Biological Conservation, 61(1), 1-10.
Laffan, S. W., & Crisp, M. D. (2003). Assessing endemism at multiple spatial scales, with an example from the Australian vascular flora. Journal of Biogeography, 30(4), 511-520.
Rosauer, D. A. N., Laffan, S. W., Crisp, M. D., Donnellan, S. C., & Cook, L. G. (2009). Phylogenetic endemism: a new approach for identifying geographical concentrations of evolutionary history. Molecular Ecology, 18(19), 4061-4072.
Allen, B., Kon, M., & Bar-Yam, Y. (2009). A new phylogenetic diversity measure generalizing the Shannon index and its application to phyllostomid bats. The American Naturalist, 174(2), 236-243.
Chao, A., Chiu, C. H., & Jost, L. (2010). Phylogenetic diversity measures based on Hill numbers. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 365(1558), 3599-3609.
Mishler, B. D., Knerr, N., González-Orozco, C. E., Thornhill, A. H., Laffan, S. W., & Miller, J. T. (2014). Phylogenetic measures of biodiversity and neo-and paleo-endemism in Australian Acacia. Nature Communications, 5(1), 4473.
Tucker, C. M., Cadotte, M. W., Davies, T. J., et al. (2016) A guide to phylogenetic metrics for conservation, community ecology and macroecology. Biological Reviews, 92(2), 698-715.
Kling, M. M., Mishler, B. D., Thornhill, A. H., Baldwin, B. G., & Ackerly, D. D. (2019). Facets of phylodiversity: evolutionary diversification, divergence and survival as conservation targets. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B, 374(1763), 20170397.
Examples
ps <- ps_simulate()
div <- ps_diversity(ps)
terra::plot(div)