Creates 3D voxel visualizations from sparse 3D point data. Each data point becomes a fixed-size cube centered on its coordinates. Useful for volumetric data and 3D pixel art.
Usage
stat_voxel_3d(
mapping = NULL,
data = NULL,
geom = GeomPolygon3D,
position = "identity",
width = 1,
faces = "all",
light = lighting(),
na.rm = FALSE,
show.legend = NA,
inherit.aes = TRUE,
...
)Arguments
- mapping
Set of aesthetic mappings created by
aes().- data
The data to be displayed in this layer.
- geom
The geometric object to use display the data. Defaults to GeomPolygon3D for proper 3D depth sorting.
- position
Position adjustment, defaults to "identity".
- width
Numeric value controlling voxel size as a fraction of grid spacing. Default is 1.0 (voxels touch each other). Use 0.8 for small gaps, 1.2 for overlap. Grid spacing is determined automatically using
resolution()for each dimension.- faces
Character vector specifying which faces to render. Options:
"all"(default): Render all 6 faces"none": Render no facesVector of face names:
c("zmax", "xmin", "ymax"), etc.
Valid face names: "xmin", "xmax", "ymin", "ymax", "zmin", "zmax".
- light
A lighting specification object created by
lighting()- na.rm
If
FALSE, missing values are removed with a warning.- show.legend
Logical indicating whether this layer should be included in legends.
- inherit.aes
If
FALSE, overrides the default aesthetics.- ...
Other arguments passed on to
layer().
Aesthetics
stat_voxel_3d() requires the following aesthetics:
x: X coordinate (voxel center position)
y: Y coordinate (voxel center position)
z: Z coordinate (voxel center position)
And understands these additional aesthetics:
fill: Voxel fill color
colour: Voxel border color
alpha: Voxel transparency
Computed variables
light: Computed lighting value (numeric for most methods, hex color fornormal_rgb)normal_x,normal_y,normal_z: Face normal componentsgroup: Hierarchical group identifier with format "voxel_XXXX__face_type" for proper depth sortingvoxel_id: Sequential voxel numberface_type: Face name ("zmax", "xmin", etc.)
See also
stat_pillar_3d() for variable-height columns, stat_surface_3d() for smooth surfaces,
coord_3d() for 3D coordinate systems, lighting() for lighting specifications,
GeomPolygon3D for the default geometry.
Examples
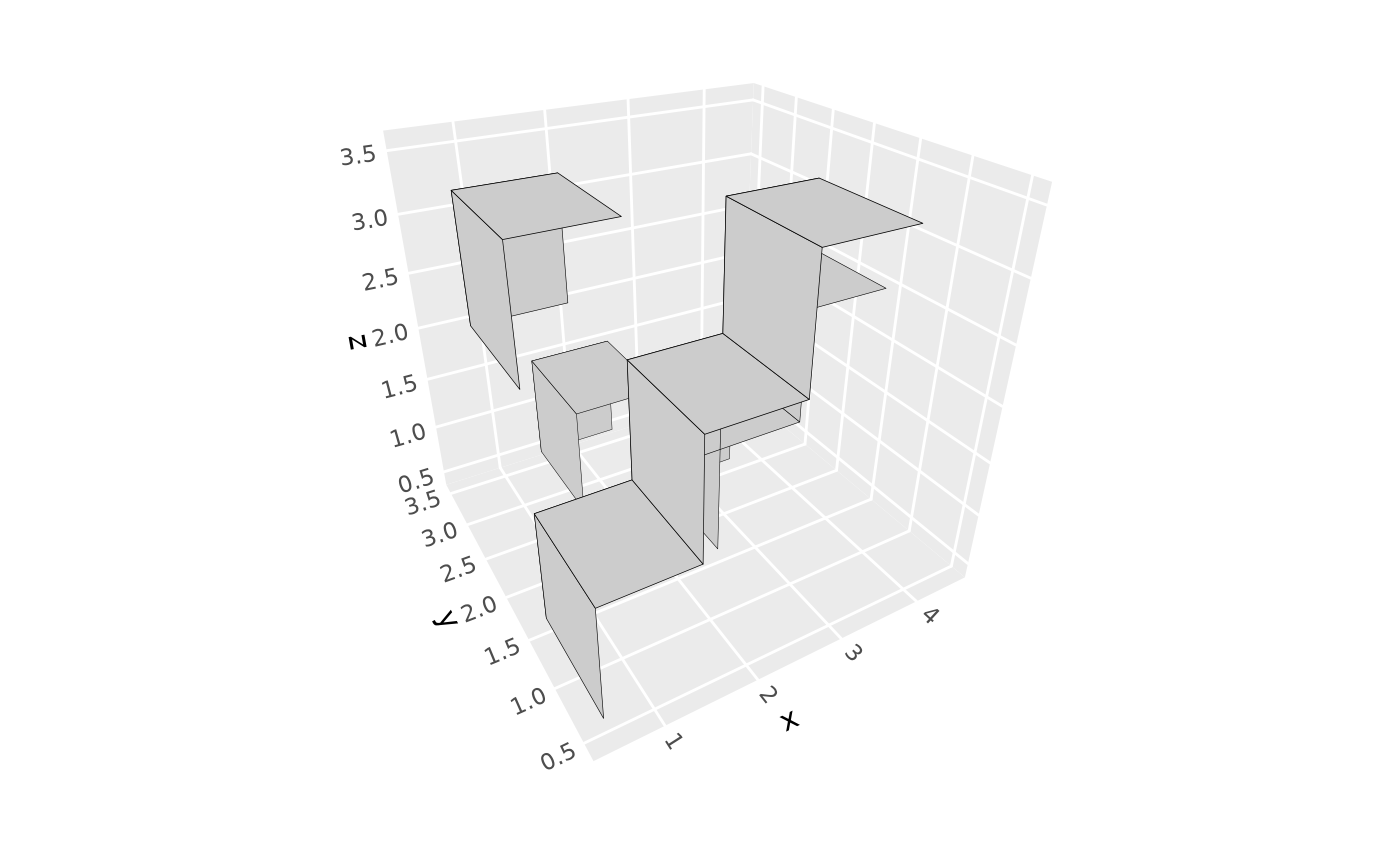
# Sparse 3D voxel data
voxel_data <- data.frame(
x = c(1, 2, 3, 2, 1, 3, 4),
y = c(1, 1, 2, 3, 2, 1, 2),
z = c(1, 2, 1, 1, 3, 3, 2)
)
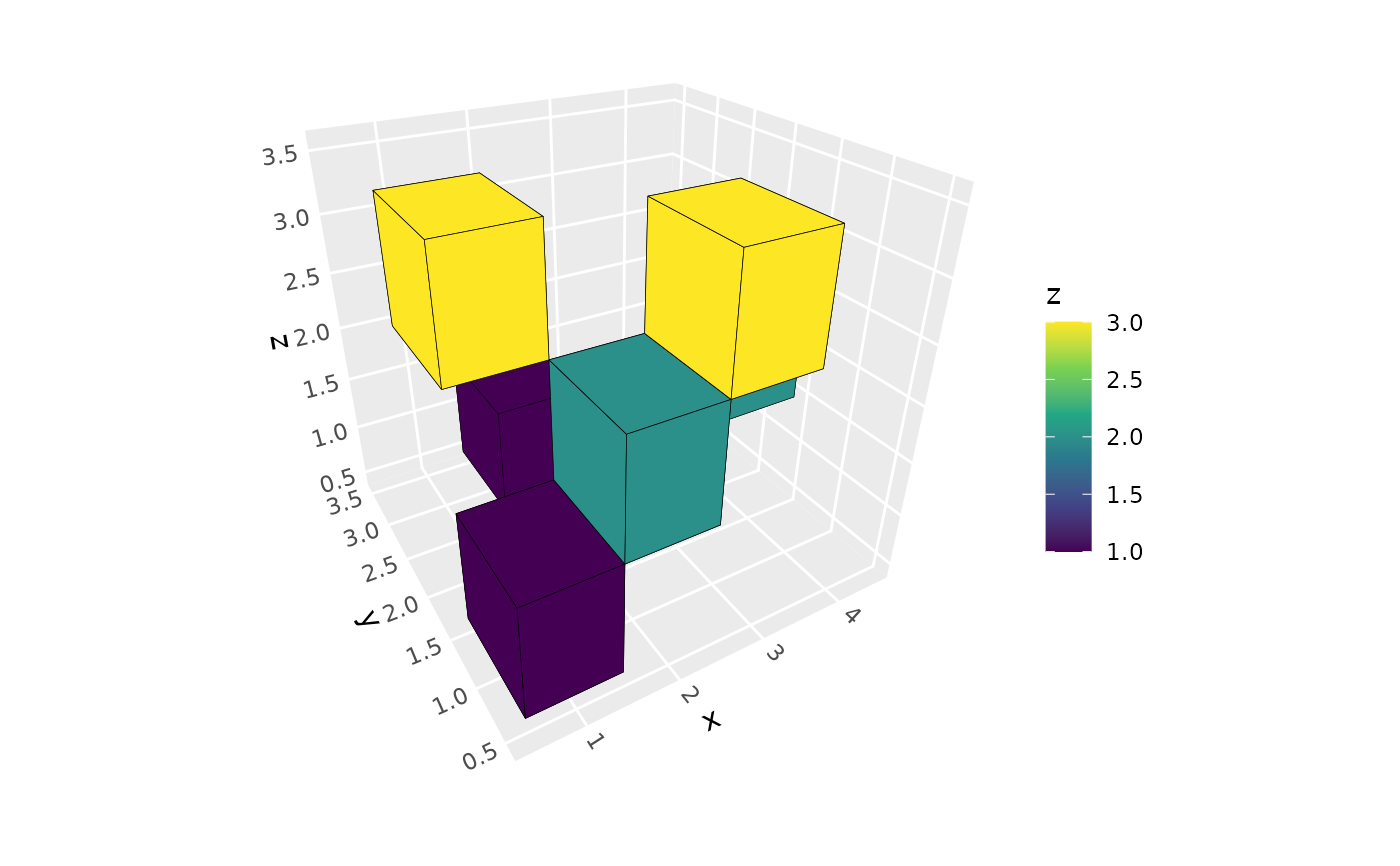
p <- ggplot(voxel_data, aes(x, y, z)) + coord_3d()
# Basic 3D voxel plot
p + stat_voxel_3d(aes(fill = z), color = "black") +
scale_fill_viridis_c()
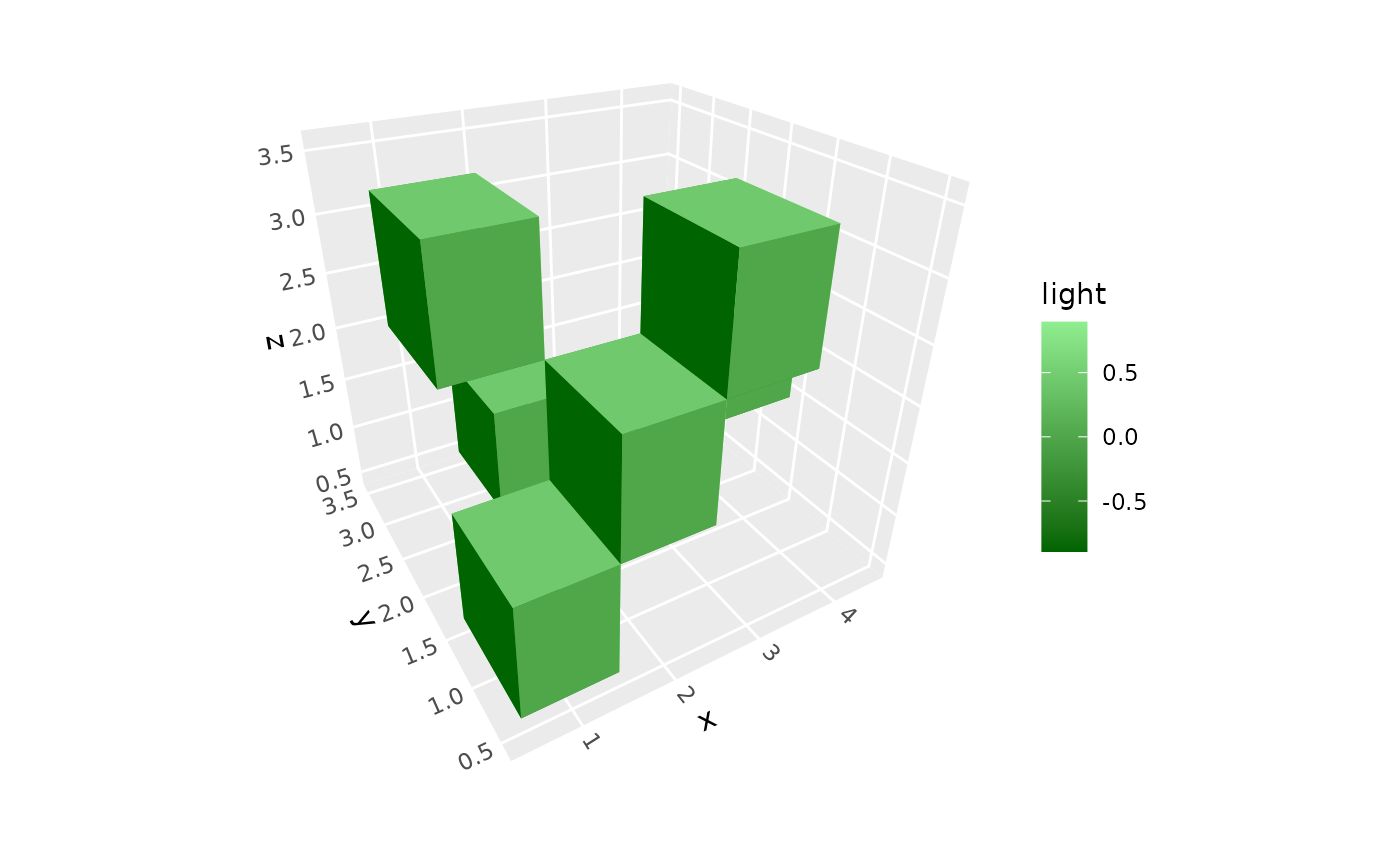
 # Directional lighting (like sunlight)
p + stat_voxel_3d(aes(fill = after_stat(light)),
light = lighting(direction = c(1, 0, .5))) +
scale_fill_gradient(low = "darkgreen", high = "lightgreen")
# Directional lighting (like sunlight)
p + stat_voxel_3d(aes(fill = after_stat(light)),
light = lighting(direction = c(1, 0, .5))) +
scale_fill_gradient(low = "darkgreen", high = "lightgreen")
 # Show only visible faces for performance
p + stat_voxel_3d(faces = c("zmax", "ymax", "xmin"), color = "black")
# Show only visible faces for performance
p + stat_voxel_3d(faces = c("zmax", "ymax", "xmin"), color = "black")