Creates 3D surfaces by fitting smooth models to scattered (x,y,z) data points. The fitted model is evaluated on a regular grid and rendered as a 3D surface with optional standard error surfaces and lighting effects.
Usage
stat_smooth_3d(
mapping = NULL,
data = NULL,
geom = GeomSmooth3D,
position = "identity",
method = "loess",
formula = NULL,
method.args = list(),
xlim = NULL,
ylim = NULL,
n = 30,
se = FALSE,
level = 0.95,
se.fill = NULL,
se.colour = NULL,
se.color = NULL,
se.alpha = 0.5,
se.linewidth = NULL,
light = lighting(),
na.rm = FALSE,
show.legend = NA,
inherit.aes = TRUE,
...
)Arguments
- mapping
Set of aesthetic mappings created by
aes(). This stat requiresx,y, andzaesthetics from the input data. By default, fill is mapped toafter_stat(fitted).- data
The data to be displayed in this layer. Must contain x, y, z columns.
- geom
The geometric object to use display the data. Defaults to GeomPolygon3D for proper 3D depth sorting.
- position
Position adjustment, defaults to "identity".
- method
Smoothing method to use. Currently supported:
"loess"(default): Local polynomial regression"lm": Linear model"glm": Generalized linear model"gam": Generalized additive model (requiresmgcvpackage)
- formula
Model formula. If
NULL(default), uses method-appropriate defaults:z ~ x + yfor lm and glm,z ~ s(x) + s(y)for gam, auto for loess.- method.args
List of additional arguments passed to the fitting function. For loess, this might include
spanordegree. For lm, this might includeweights. For glm, this might includefamily(defaults togaussian()). For gam, this might include smoothing parameters or basis specifications.- xlim, ylim
Numeric vectors of length 2 giving the range for prediction grid. If
NULL(default), uses the exact data range with no extrapolation, followinggeom_smooth()conventions.- n
Either a single integer specifying grid resolution in both dimensions, or a vector of length 2 specifying
c(nx, ny)for different resolutions. Default is 30. Higher values create smoother surfaces but slower rendering.- se
Logical indicating whether to display confidence interval bands around the smooth; if
TRUE, these are rendered as additional surfaces; they inherit aesthetics from the primary smooth layer unless otherwise specified. Defaults toFALSE.- level
Level of confidence interval to use (0.95 by default).
- se.fill
Fill colour for confidence interval bands. If
NULL, inherits from the main surfacefillaesthetic.- se.colour, se.color
Colour for confidence interval band borders. If
NULL, inherits from the main surfacecolouraesthetic.- se.alpha
Alpha transparency for confidence interval bands. Defaults to 0.5.
- se.linewidth
Line width for confidence interval band borders. If
NULL, inherits from the main surfacelinewidthaesthetic.- light
A lighting specification object created by
lighting()- na.rm
If
TRUE, removes missing values before fitting the model. IfFALSE, missing values will cause an error. Default isFALSE.- show.legend
Logical indicating whether this layer should be included in legends.
- inherit.aes
If
FALSE, overrides the default aesthetics.- ...
Other arguments passed on to
layer(), such ascolour,fill,linewidth, etc..
Aesthetics
stat_smooth_3d() requires the following aesthetics from input data:
x: X coordinate
y: Y coordinate
z: Z coordinate (response variable to be smoothed)
Computed variables
x,y,z: Grid coordinates and smoothed predictionsfitted: Smoothed predictions (same aszwhenlevel == "fitted")se: Standard errors of the fitted values (available whense = TRUE)level: Type of surface ("fitted", "upper CI", or "lower CI" for confidence bands)light: Computed lighting value (numeric for most methods, hex color fornormal_rgb)normal_x,normal_y,normal_z: Surface normal componentsslope: Gradient magnitude from surface calculationsaspect: Direction of steepest slope from surface calculationsdzdx,dzdy: Partial derivatives from surface calculations
See also
stat_surface_3d() for surfaces from existing grid data,
stat_function_3d() for mathematical function surfaces,
lighting() for lighting specifications, coord_3d() for 3D coordinate systems.
Examples
library(ggplot2)
# Generate scattered 3D data
set.seed(123)
d <- data.frame(
x = runif(100, -2, 2),
y = runif(100, -2, 2)
)
d$z <- abs(1 + d$x^2 - d$y^2 + rnorm(100, 0, 1))
# Base plot
p <- ggplot(d, aes(x, y, z)) + coord_3d()
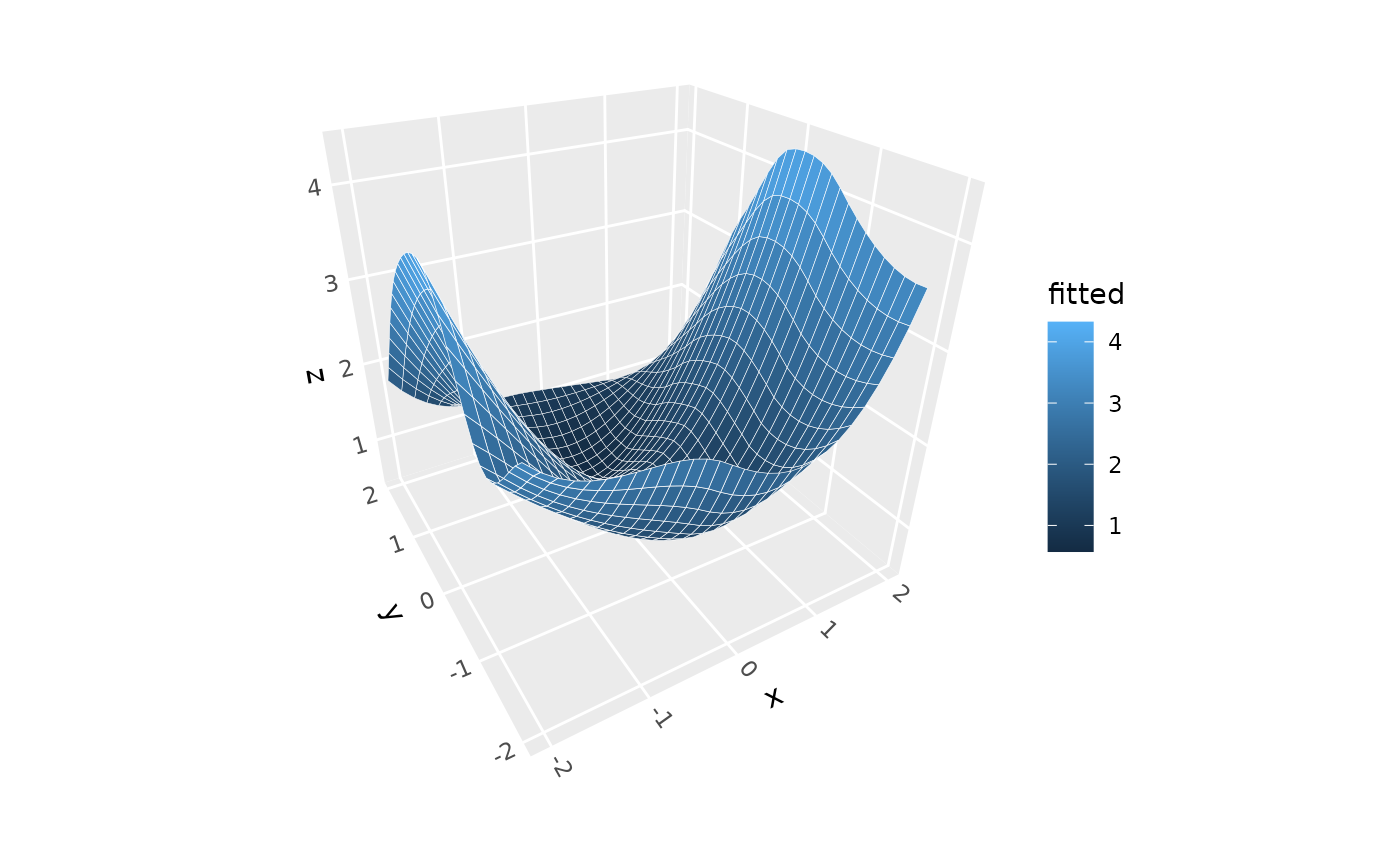
# Basic smooth surface with default loess model
p + stat_smooth_3d()
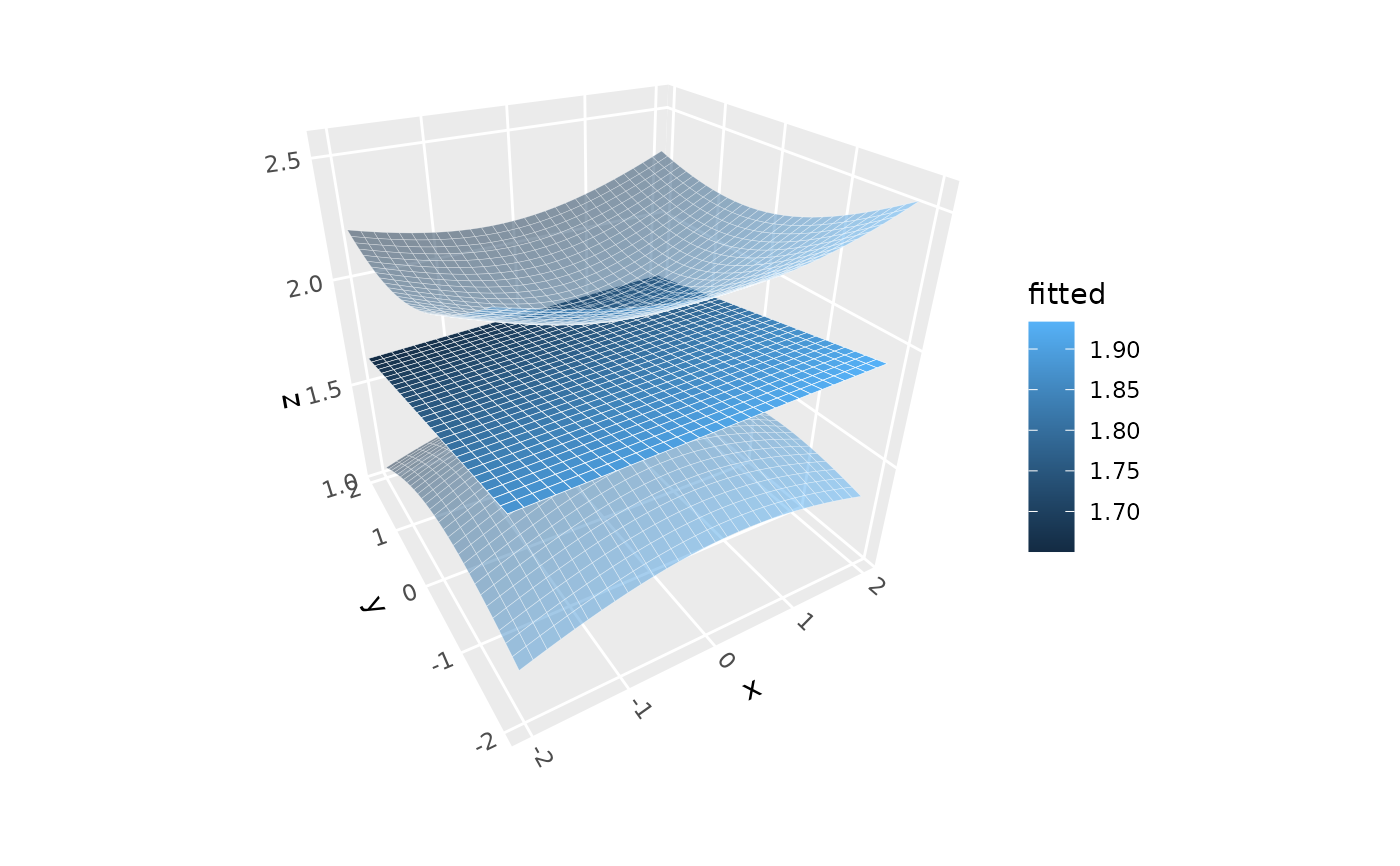
 # Linear model surface with 90% confidence intervals
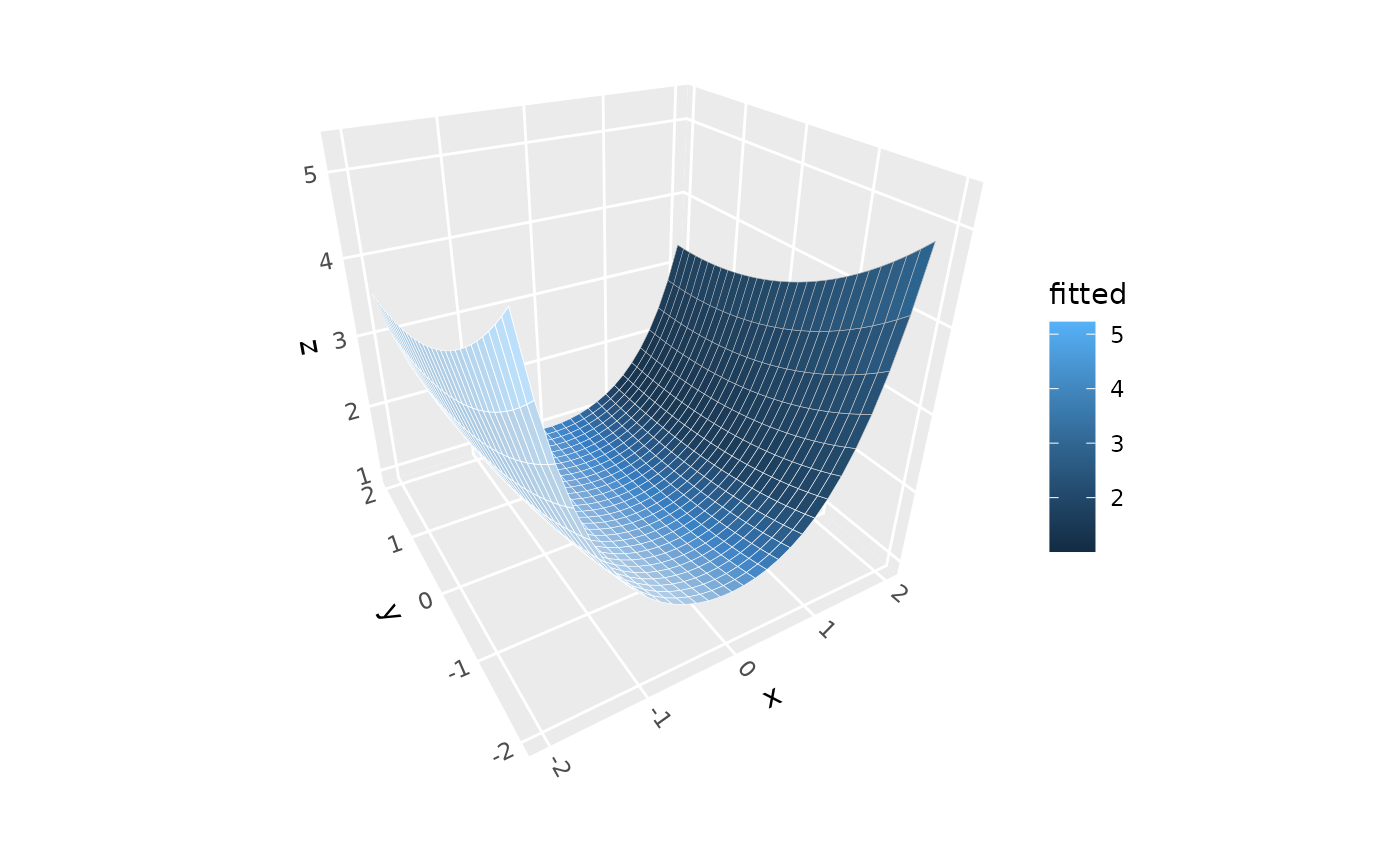
p + stat_smooth_3d(method = "lm", se = TRUE, level = 0.9)
# Linear model surface with 90% confidence intervals
p + stat_smooth_3d(method = "lm", se = TRUE, level = 0.9)
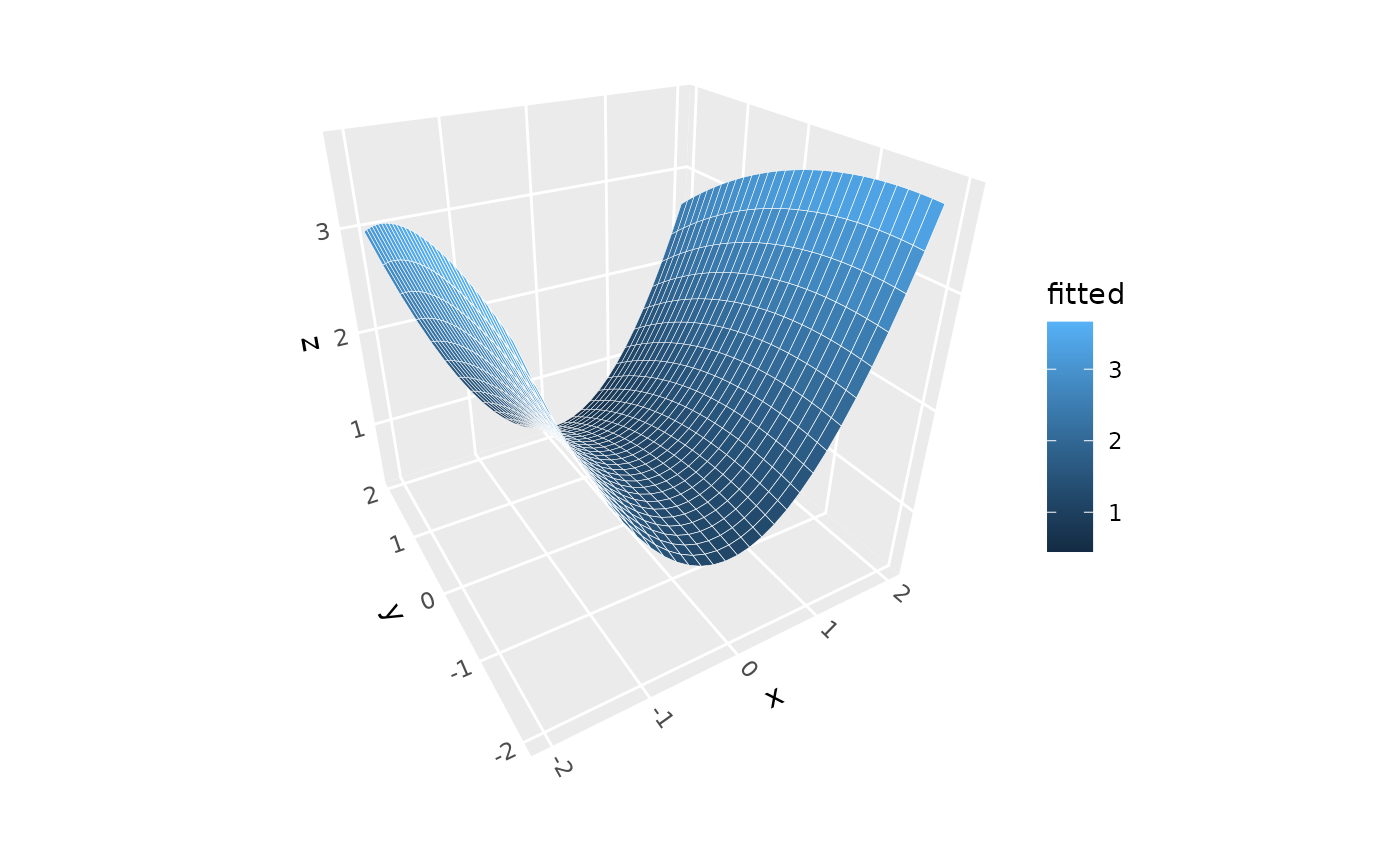
 # Linear model surface with custom model formula
p + stat_smooth_3d(method = "lm",
formula = z ~ poly(x, 2) + poly(y, 2) + x:y)
# Linear model surface with custom model formula
p + stat_smooth_3d(method = "lm",
formula = z ~ poly(x, 2) + poly(y, 2) + x:y)
 # Loess with custom span parameter, and lighting aesthetics
p + stat_smooth_3d(method = "loess", method.args = list(span = 0.3),
fill = "steelblue", color = "white",
light = lighting(blend = "both"))
# Loess with custom span parameter, and lighting aesthetics
p + stat_smooth_3d(method = "loess", method.args = list(span = 0.3),
fill = "steelblue", color = "white",
light = lighting(blend = "both"))
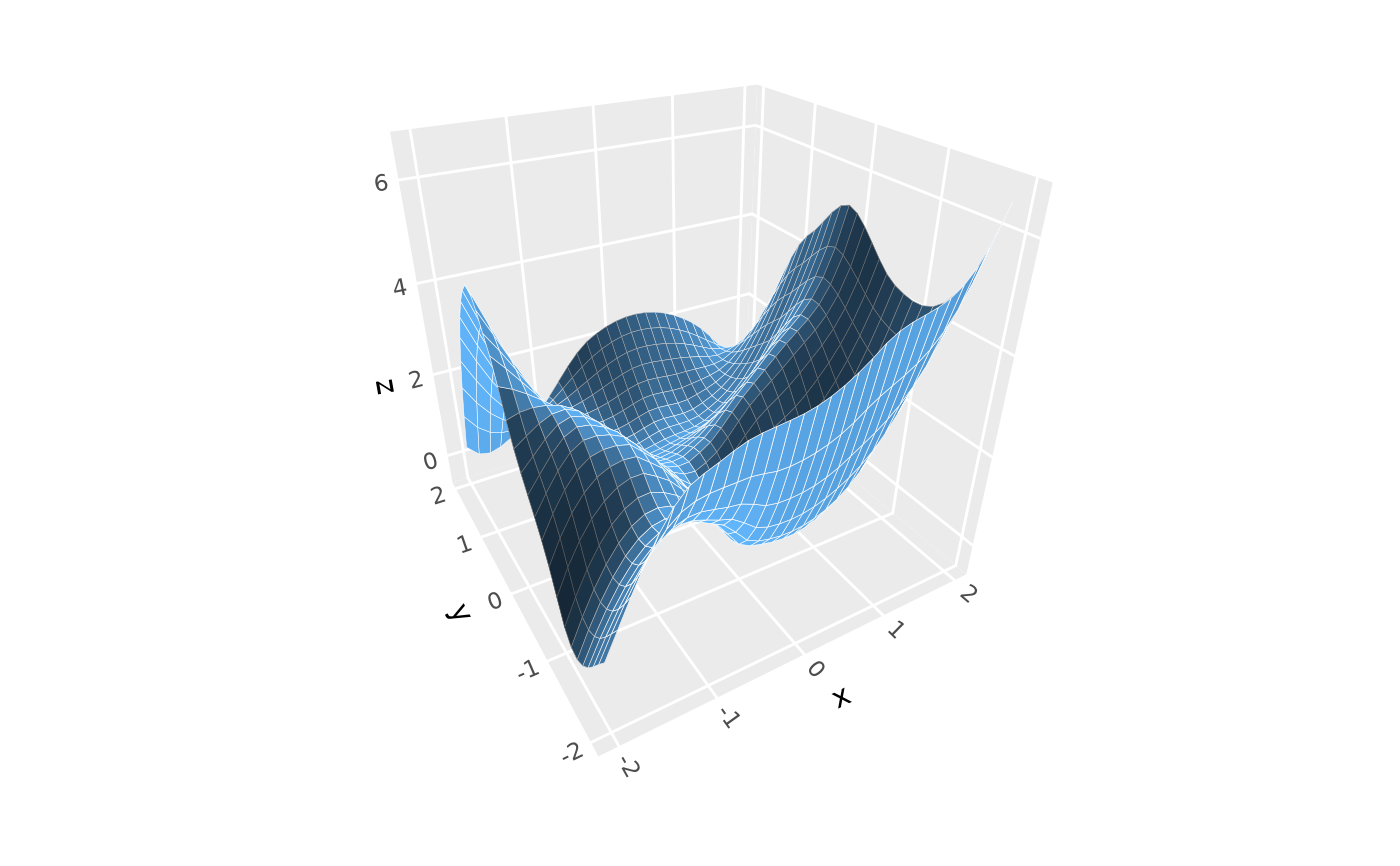 # GLM with Gamma family for positive data
p + stat_smooth_3d(
method = "glm",
method.args = list(family = Gamma(link = "log")),
formula = z ~ poly(x, 2) + poly(y, 2),
light = lighting(blend = "both", blend_mode = "hsl", blend_strength = .8))
# GLM with Gamma family for positive data
p + stat_smooth_3d(
method = "glm",
method.args = list(family = Gamma(link = "log")),
formula = z ~ poly(x, 2) + poly(y, 2),
light = lighting(blend = "both", blend_mode = "hsl", blend_strength = .8))
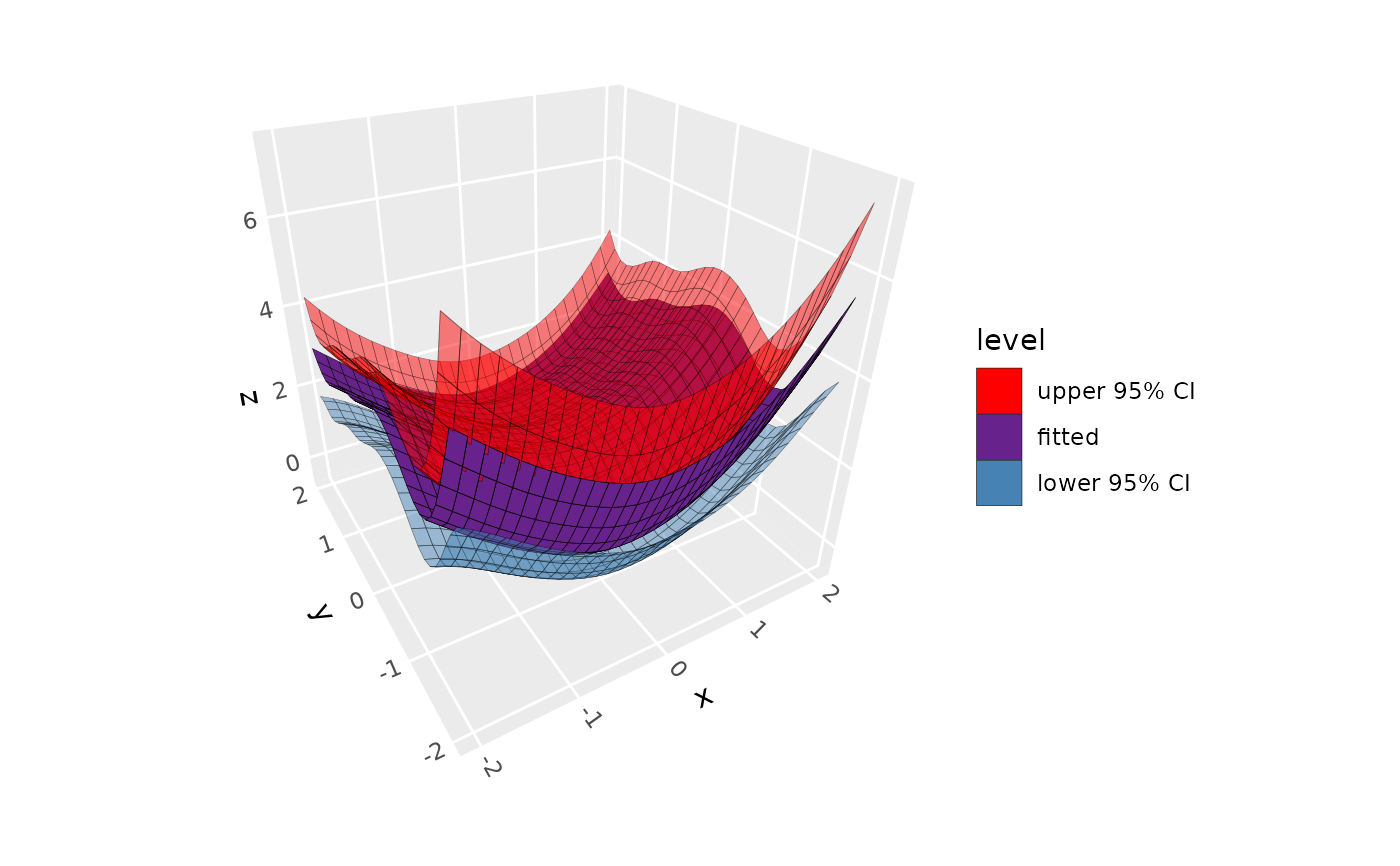
 # GAM with default smoothers, with fill colored by uncertainty layer
p + stat_smooth_3d(aes(fill = after_stat(level)),
method = "gam", se = TRUE, color = "black") +
scale_fill_manual(values = c("red", "darkorchid4", "steelblue"))
# GAM with default smoothers, with fill colored by uncertainty layer
p + stat_smooth_3d(aes(fill = after_stat(level)),
method = "gam", se = TRUE, color = "black") +
scale_fill_manual(values = c("red", "darkorchid4", "steelblue"))
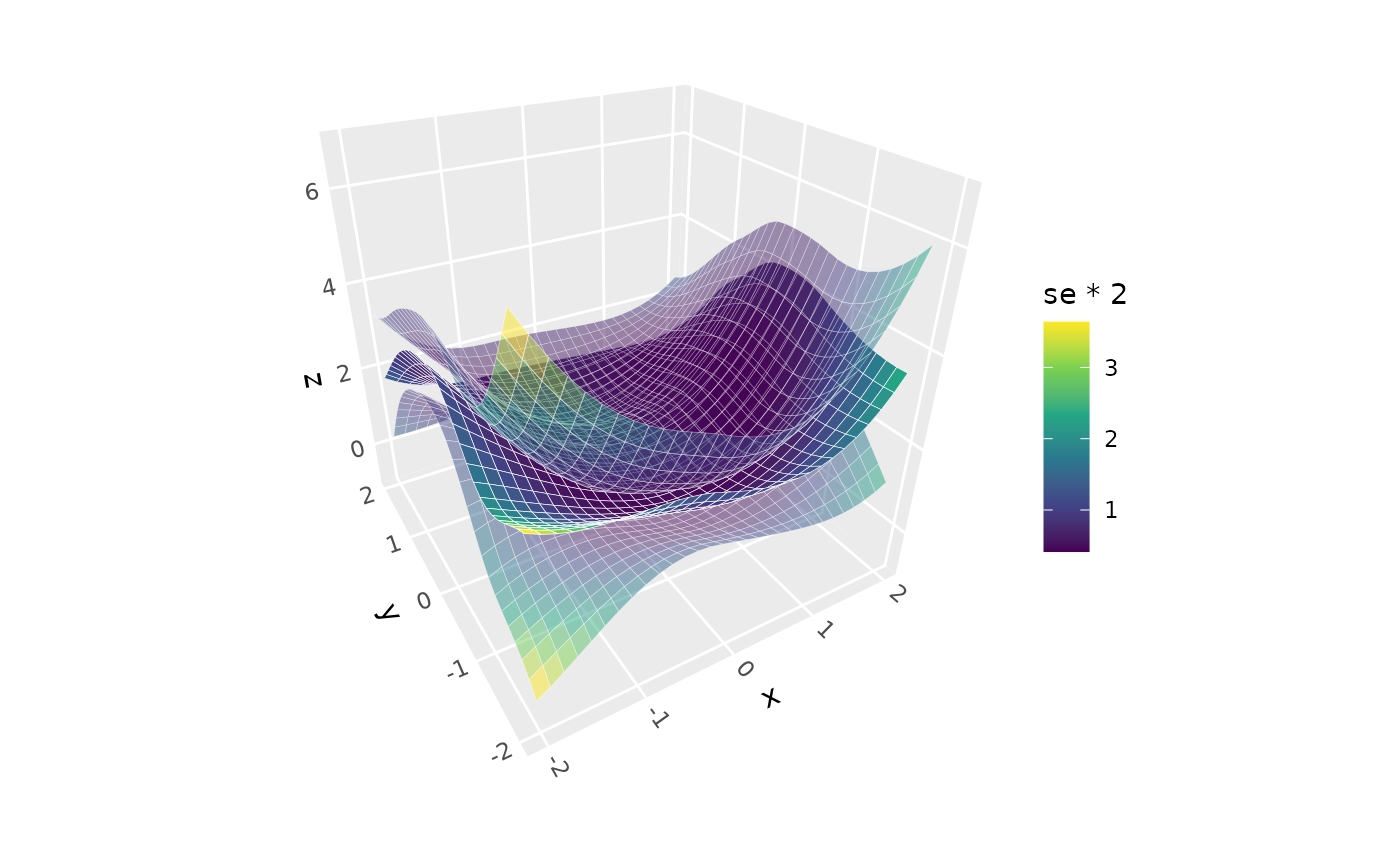
 # Color surface bands by uncertainty
p + stat_smooth_3d(aes(fill = after_stat(se * 2)), se = TRUE) +
scale_fill_viridis_c()
# Color surface bands by uncertainty
p + stat_smooth_3d(aes(fill = after_stat(se * 2)), se = TRUE) +
scale_fill_viridis_c()
 # Extend surface beyond data range (explicit extrapolation)
p + stat_smooth_3d(method = "lm",
xlim = c(-3, 3), ylim = c(-3, 3))
# Extend surface beyond data range (explicit extrapolation)
p + stat_smooth_3d(method = "lm",
xlim = c(-3, 3), ylim = c(-3, 3))
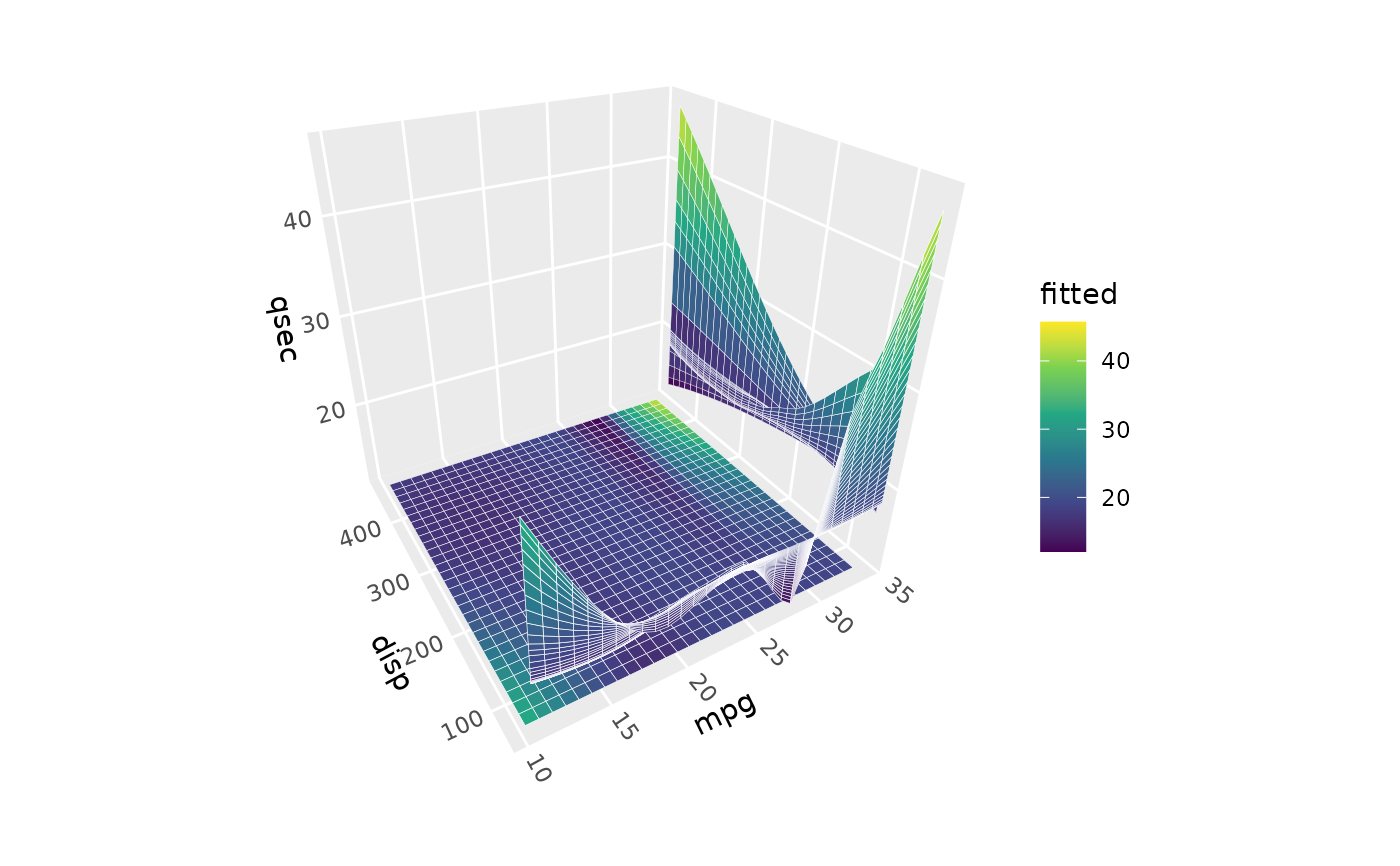
 # Project 2D views of the surface onto face panels
ggplot(mtcars, aes(mpg, disp, qsec)) +
stat_smooth_3d(position = position_on_face(faces = c("xmax", "ymin", "zmin"))) +
scale_fill_viridis_c() +
coord_3d()
# Project 2D views of the surface onto face panels
ggplot(mtcars, aes(mpg, disp, qsec)) +
stat_smooth_3d(position = position_on_face(faces = c("xmax", "ymin", "zmin"))) +
scale_fill_viridis_c() +
coord_3d()