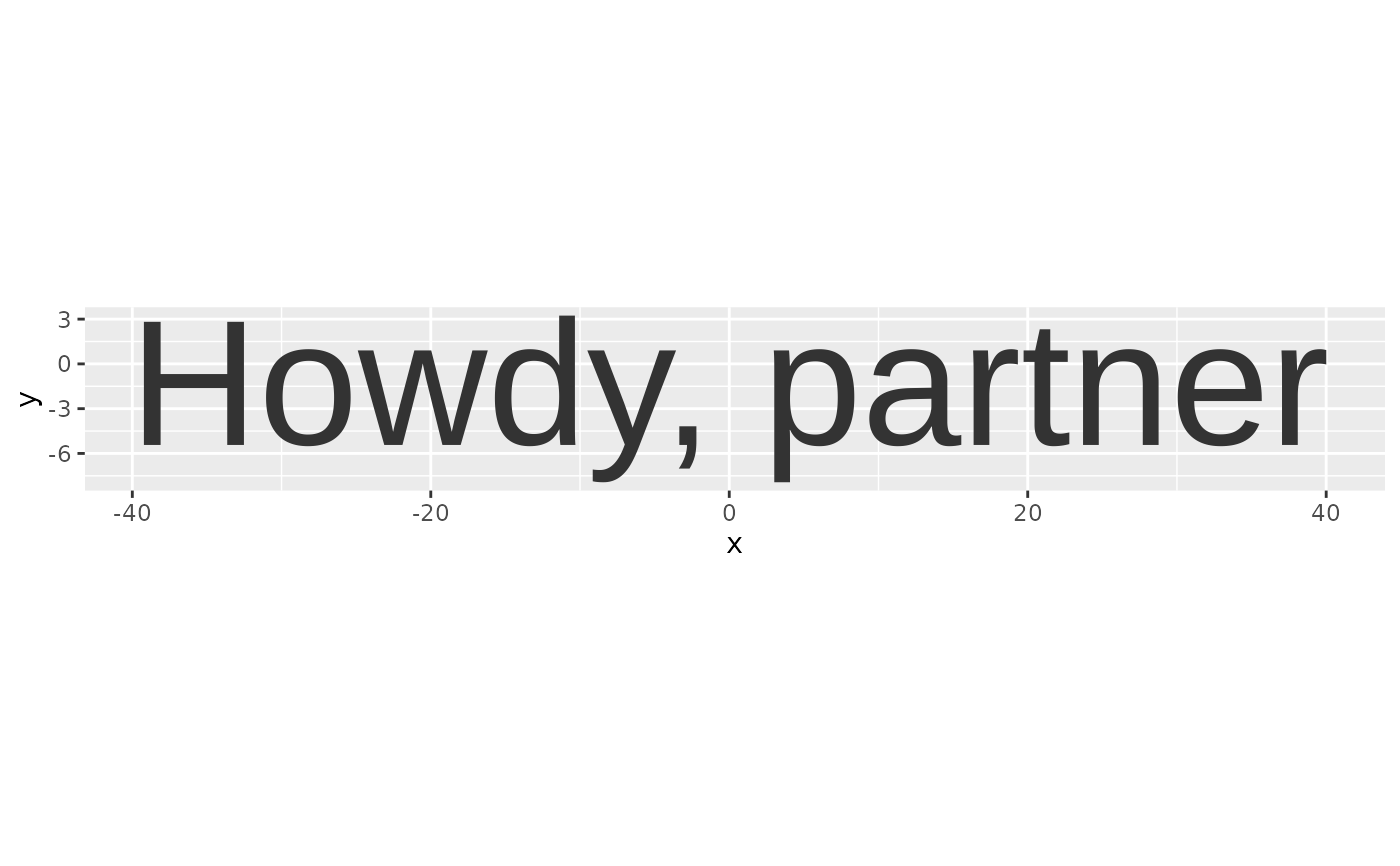Converts a text string into polygon vertices suitable for plotting with ggplot2's geom_polygon. Uses systemfonts for font matching and glyph extraction.
Usage
text_outlines(
text,
family = "sans",
weight = "normal",
italic = FALSE,
size = 12,
tolerance = 0.01,
spacing = 0,
hjust = 0.5,
vjust = 0.5,
width = NA,
align = "left",
lineheight = 1,
internal_size = 144
)Arguments
- text
Character string to convert
- family
Font family name (e.g., "Arial", "Helvetica", "sans")
- weight
Font weight ("normal", "bold", "thin", "light", etc.)
- italic
Logical; use italic variant
- size
Font size in points
- tolerance
Bezier curve tolerance; lower values give more detailed outlines
- spacing
Additional letter spacing in em units
- hjust, vjust
The justification of the textbox surrounding the text
- width
Maximum line width in inches for word wrapping; NA disables wrapping
- align
Text alignment: "left", "center", or "right"
- lineheight
Line height multiplier
- internal_size
Internal rendering size for kerning precision; generally shouldn't need adjustment
Value
A data frame with columns: x, y, contour, glyph, letter, poly_id. X and y are vertex coordinates, in point units.
Examples
text_outlines("Howdy, partner", family = "Arial") |>
ggplot2::ggplot(ggplot2::aes(x, y, group = letter, subgroup = poly_id)) +
ggplot2::geom_polygon() +
ggplot2::coord_fixed()